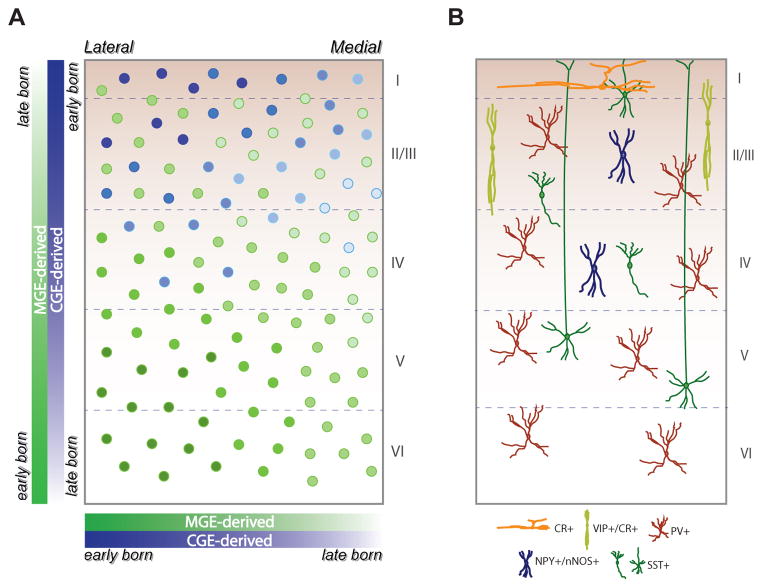
Figure I. The developmental distribution of interneuron subtypes.
(A) Schematic of a coronal section through the mouse neonatal cerebral cortex showing the areal and laminar positioning of MGE- and CGE-derived GABAergic interneurons. Both MGE- and CGE-derived interneurons reach their final areal positions in a lateral to medial gradient (i.e., arriving first in laternal regions of cortex). MGE-derived interneurons show an inside-out pattern of distribution, whereas CGE-derived interneurons exhibit an outside-in pattern of distribution. MGE-derived interneurons distribute relatively evenly in the neocortex, whereas CGE-derived interneurons preferentially distribute in superficial layers. (B) Laminar distribution of main subtypes of interneurons. PV+ interneurons are abundant throughout cortical layers II–VI. SST+ interneurons mainly localize to layers II–V. CR+ interneurons preferentially distribute in layer I. VIP+/CR+ interneurons preferentially distribute through layer II/III. NPY+/nNOS+ interneurons mainly localize to layers II–IV. PV, parvalbumin; SST, somatostatin; CR, calretinin; VIP, vasoactive intestinal polypeptide; NPY, neuropeptide Y; nNOS, neuronal nitric oxide synthase. I–VI: cortical layers.