Abstract
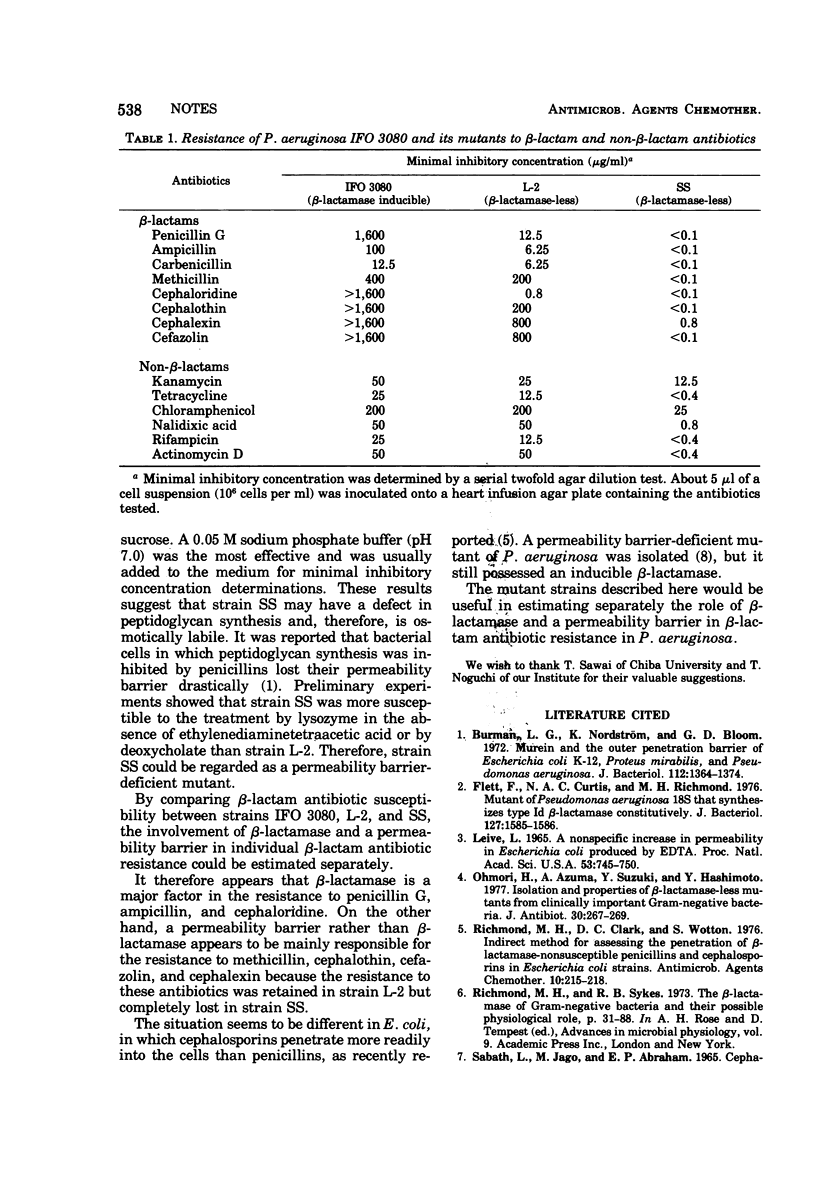
A temperature-sensitive mutant, strain SS, which is assumed to be devoid of β-lactamase activity and deficient in a permeability barrier to antibiotics, was isolated from a β-lactamase-less mutant, strain L-2, derived from Pseudomonas aeruginosa IFO 3080. By comparing the β-lactam antibiotic susceptibility between strains IFO 3080, L-2, and SS, the involvement of both β-lactamase and a permeability barrier in determining the β-lactam antibiotic resistance was estimated.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burman L. G., Nordström K., Bloom G. D. Murein and the outer penetration barrier of Escherichia coli K-12, Proteus mirabilis, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1972 Dec;112(3):1364–1374. doi: 10.1128/jb.112.3.1364-1374.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flett F., Curtis N. A., Richmond M. H. Mutant of Pseudomonas aeruginosa 18S that synthesizes type Id beta-lactamase constitutively. J Bacteriol. 1976 Sep;127(3):1585–1586. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.3.1585-1586.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEIVE L. A NONSPECIFIC INCREASE IN PERMEABILITY IN ESCHERICHIA COLI PRODUCED BY EDTA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Apr;53:745–750. doi: 10.1073/pnas.53.4.745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohmori H., Azuma A., Suzuki Y., Hashimoto Y. Isolation and properties of beta-lactamase-less mutants from clinically important gram-negative bacteria. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1977 Mar;30(3):267–269. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.30.267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richmond M. H., Clark D. C., Wotton S. Indirect method for assessing the penetration of beta-lactamase-nonsusceptible penicillins and cephalosporins in Escherichia coli strains. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Aug;10(2):215–218. doi: 10.1128/aac.10.2.215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richmond M. H., Sykes R. B. The beta-lactamases of gram-negative bacteria and their possible physiological role. Adv Microb Physiol. 1973;9:31–88. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(08)60376-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sykes R. B. Resistance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to antimicrobial drugs. Prog Med Chem. 1975;12:333–393. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6468(08)70180-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamaki S., Sato T., Matsuhashi M. Role of lipopolysaccharides in antibiotic resistance and bacteriophage adsorption of Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1971 Mar;105(3):968–975. doi: 10.1128/jb.105.3.968-975.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


