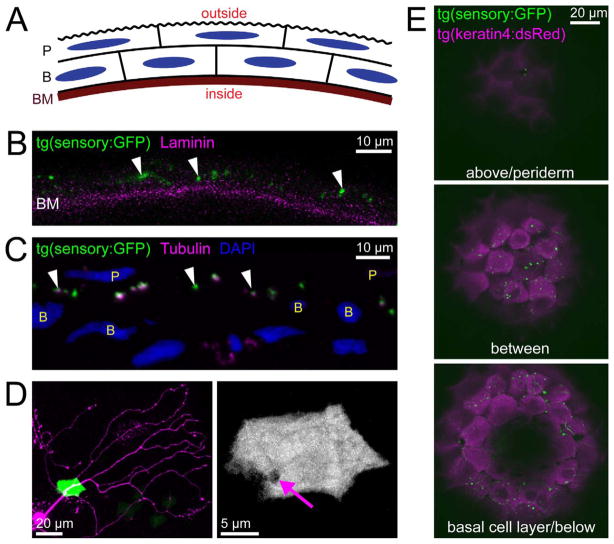
Figure 2.
Peripheral sensory axons arborize within the skin. A: Diagram of the embryonic zebrafish skin. The skin consists of two layers, the periderm (P) and basal cell layer (B). The basement membrane (BM) is located below the basal cell layer. B: Antibody stain for GFP (green) and laminin (magenta) in a vibratome section of a tg(sensory:GFP) fish at 54 hpf. GFP-expressing peripheral axons (arrowheads) localized exterior to the band of laminin staining. C: Antibody stain for GFP (green) and tubulin (magenta) in a 70-nm microtome section of a 78 hpf sensory:GFP transgenic fish. Cell nuclei labeled with DAPI (blue; P, periderm nucleus; B, basal cell nucleus). Peripheral sensory axons (arrowheads) are exclusively located between the nuclei of the two epidermal cell layers. D: By using transient transgenesis to achieve mosaic expression of both transgenes, a single sensory axon (magenta) was imaged extending its primary axon through a skin cell (green) and arborizing above it. Maximum projection of a confocal image stack taken of the head of a live embryo at 54 hpf. Right, green channel only, showing an opening in the skin cell through which the axon enters (arrow). E: Three confocal optical sections showing a dorsal view of the top of the head of an embryo harboring the sensory:GFP and keratin4:dsRED transgenes. All labeled axons arborized between the two skin layers. In the top panel, two green dots are visible, which appear to be axonal varicosities that bulge up into the optical plane of the outer layer of skin cells. Scale bars = 10 μm in B,C; 20 μm in D (left),E; 5 μm in D (right).