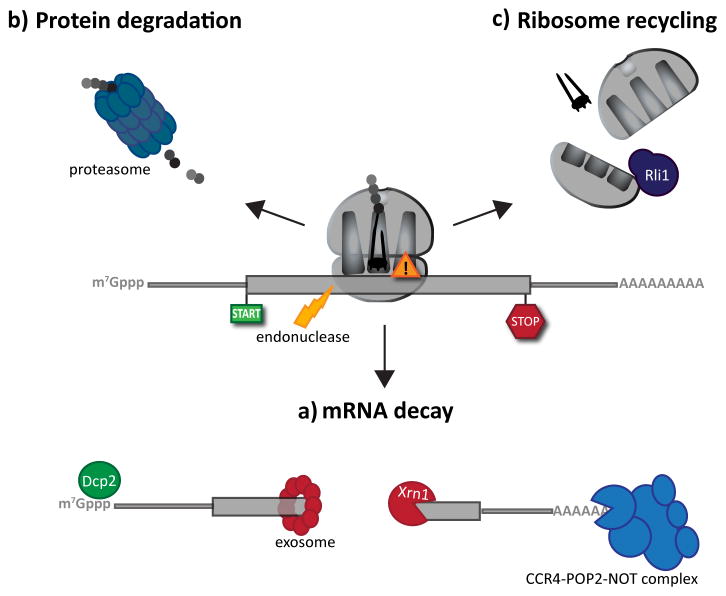
Figure 3. mRNA surveillance pathway outcomes.
Following the recognition of NMD, NGD or NSD ribosome complexes, at least three discrete salvage pathways are invoked: mRNA decay, protein degradation and ribosome recycling. (a) mRNA decay. Endonucleolytic cleavage subverts the need for deadenylation, by the CCR4-POP2-NOT complex, and decapping, by Dcp2, prior to mRNA decay. Rapid mRNA degradation then proceeds through canonical means, including 5′-3′ degradation by Xrn1 and 3′-5′ degradation by the exosome. (b) Protein degradation. Targeted degradation of aberrant peptides occurs via the ubiquitin-proteasome system. Several E3 ligases have been implicated in this process, but the molecular features of substrate recognition remain to be determined. (c) Ribosome recycling. Dom34:Hbs1 are known to exploit the canonical recycling activities of Rli1 to effect ribosome recycling during NGD and NSD. Recycling of ribosome complexes during NMD are less well-characterized, but may involve Upf1.