Figure 3.
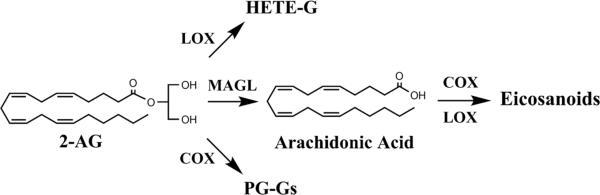
Model of 2-AG metabolism and its possible contribution to post-operative pain. Enzymes that mediate 2-AG metabolism. 2-AG metabolism occurs primarily through hydrolysis by monoacylglycerol lipase (MAGL), yielding arachidonic acid, which is subsequently converted into eicosanoids by COX and LOX enzymes. In addition, 2-AG can be metabolized into prostaglandin glycerol esters (PG-Gs) by COX-2 and hydroperoxyeicosatetraenoic acid glycerol esters (HETE-Gs) by LOX enzymes.
