Abstract
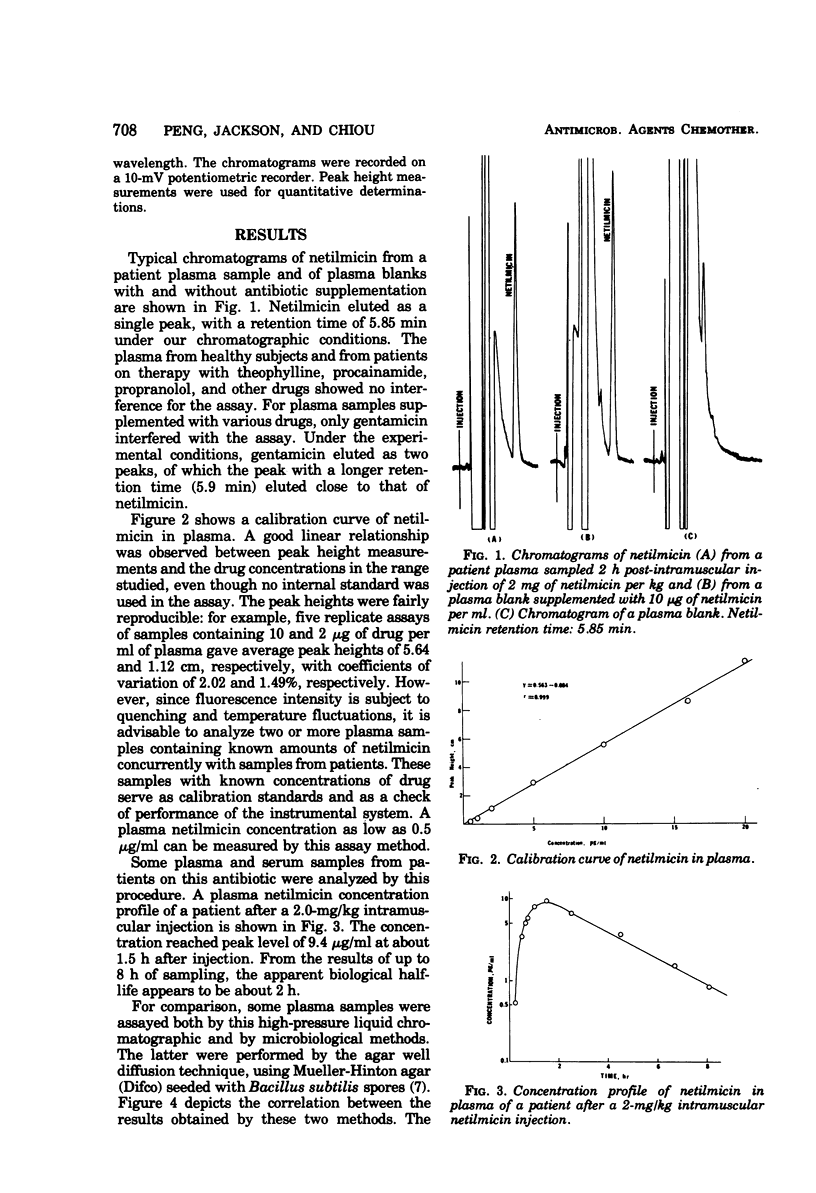
A high-pressure liquid chromatographic method for the quantitative determination of netilmicin in plasma was developed. The procedures involve acetonitrile protein precipitation, methylene chloride extraction, and dansylation to form the fluorescent dansyl derivative of netilmicin, which is extracted into ethyl acetate and chromatographed on a reverse-phase column with aqueous acetonitrile as the mobile phase. A good linear relationship between peak height measurements and netilmicin concentrations was found. This method is sensitive and reproducible; a netilmicin concentration as low as 0.5 μg/ml can be measured with only 0.1 ml of plasma sample. The results of assays of plasma or serum samples by this high-pressure liquid chromatographic method correlate well with those obtained by microbiological assays.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anhalt J. P. Assay of gentamicin in serum by high-pressure liquid chromatography. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Apr;11(4):651–655. doi: 10.1128/aac.11.4.651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barza M., Brown R. B., Shen D., Gibaldi M., Weinstein L. Predictability of blood levels of gentamicin in man. J Infect Dis. 1975 Aug;132(2):165–174. doi: 10.1093/infdis/132.2.165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiu P. J., Miller G. H., Brown A. D., Long J. F., Waitz J. A. Renal pharmacology of netilmicin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 May;11(5):821–825. doi: 10.1128/aac.11.5.821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luft F. C., Yum M. N., Kleit S. A. Comparative nephrotoxicities of netilmicin and gentamicin in rats. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Nov;10(5):845–849. doi: 10.1128/aac.10.5.845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyers B. R., Hirschman S. Z. Antimicrobial activity in vitro of netilmicin and comparison with sisomicin, gentamicin, and tobramycin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Jan;11(1):118–121. doi: 10.1128/aac.11.1.118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peng G. W., Gadalla M. A., Peng A., Smith V., Chiou W. L. High-pressure liquid-chromatographic method for determination of gentamicin in plasma. Clin Chem. 1977 Oct;23(10):1838–1844. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips I., Smith A., Shannon K. Antibacterial activity of netilmicin, a new aminoglycoside antibiotic, compared with that of gentamicin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Mar;11(3):402–406. doi: 10.1128/aac.11.3.402. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riff L. J., Moreschi G. Netilmicin and gentamicin: comparative pharmacology in humans. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Apr;11(4):609–614. doi: 10.1128/aac.11.4.609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schumacher G. E. Practical pharmacokinetic techniques for drug consultation and evaluation. IV: Gentamicin blood level versus time profiles of various dosage regimens recommended for renal impairment. Am J Hosp Pharm. 1975 Mar;32(3):299–308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. A., Morgan J. R., Mogyoros M. In vitro activity of netilmicin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Feb;11(2):362–364. doi: 10.1128/aac.11.2.362. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens P., Young L. S., Hewitt W. L. 125I radioimmunoassay of netilmicin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Apr;11(4):768–770. doi: 10.1128/aac.11.4.768. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


