Figure 4. AV411 and AV1013 inhibit Tat + Morphine-induced p65 NF-ĸB nuclear translocation and causes morphological changes in astrocytes at high concentrations.
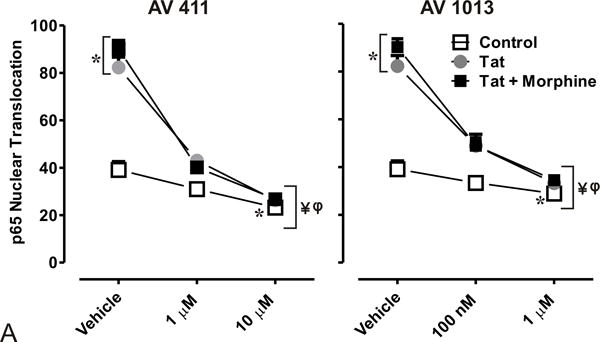
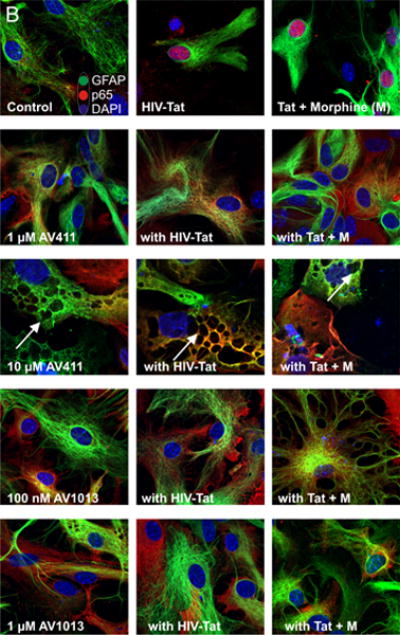
(A) Translocation of p65 in the nucleus was counted manually per 100 cells. DAPI was used as a reference for nuclear location. Total numbers were calculated using one-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni’s test for multiple comparisons. Error bars show the mean ± the SEM from 3 independent experiments. *p<0.05 vs. vehicle; ¥p<0.05 vs. Tat; φp<0.05 vs. Tat + morphine. (B) Nuclear translocation of the p65 subunit (red) was readily detectable by immunofluorescence and visualized using confocal microscopy. Astrocytes were labeled with the cell type specific immunofluorescent markers, glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP; green) and their nuclei counterstained with DAPI (blue). Magnification = 63X.
