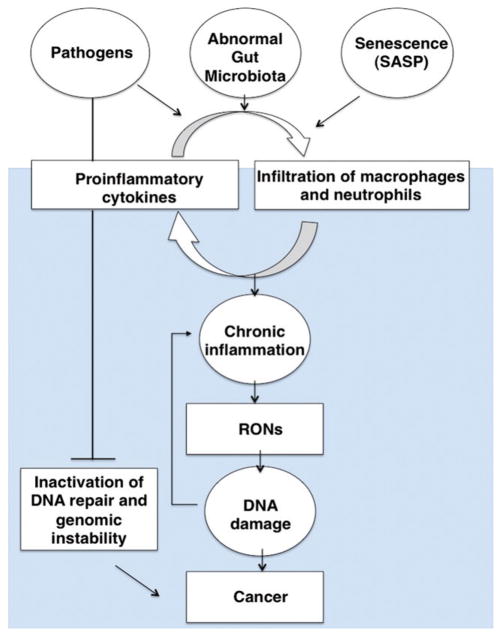
Figure 3.
A model of the links between DNA damage and inflammation. Activation of the immune response occurs as a result of infection with pathogens, exposure to the microbiota of the gut and the secretory associated senescence phenotype (SASP). Acute inflammation can lead to chronic inflammation as described in this review, resulting in the generation of RONs and leading to DNA damage. Pathogens, genetic mutations in DNA repair genes and environment-associated expression of miRNAs can inactivate DNA repair, which results in a mutator phenotype, genomic instability and cancer. (see colour version of this figure at www.informahealthcare.com/bmg).