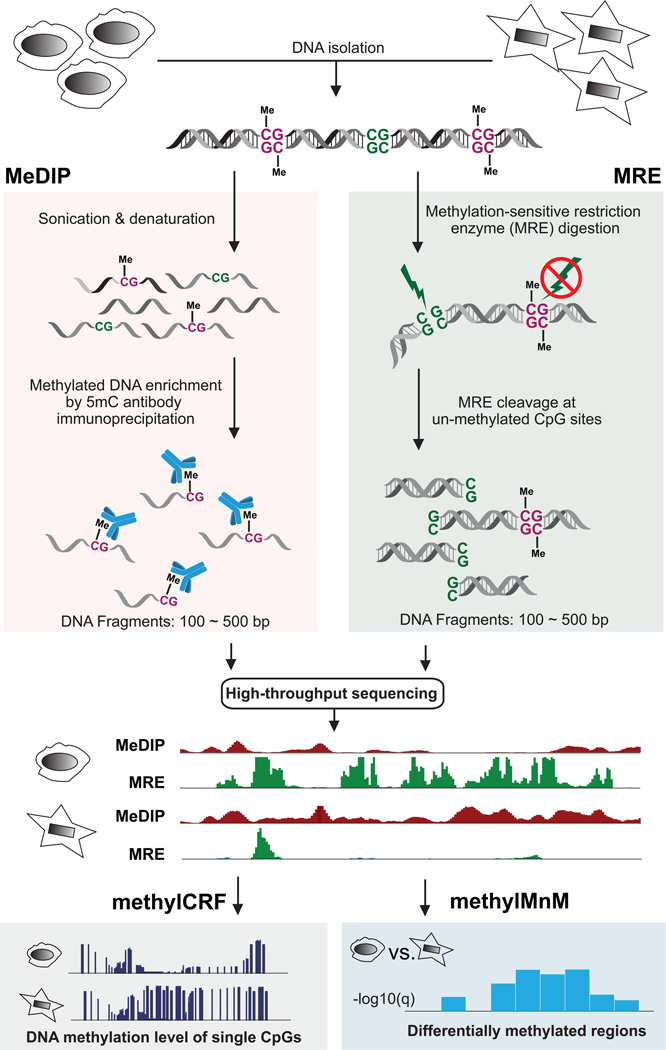
Figure 1. Workflow of combining MeDIP-seq and MRE-seq.
Genomic DNA is isolated and purified. On the MeDIP-seq side, genomic DNA is sonicated to a specific size range, and a monoclonal anti-5’methylcytosine antibody is used to enrich for methylated DNA fragments. Immunoprecipitated DNA fragments are then sequenced and mapped back to the reference genome assembly to review methylated regions. On the MRE-seq side, several methylation sensitive restriction endonucleases are used to digest intact genomic DNA. The resulting DNA fragments are then size-selected and sequenced. When mapped back to the reference genome assembly, these sequencing reads can reveal locations of unmethylated CpG sites which are located within recognition sites of specific restriction enzymes. MeDIP-seq and MRE-seq data can then be integrated by applying methylCRF, which transform enrichment-based DNA methylation data to methylation level at single CpG resolution across the genome. To compare two samples and detect differentially methylated regions, M&M is applied in a region-specific fashion.