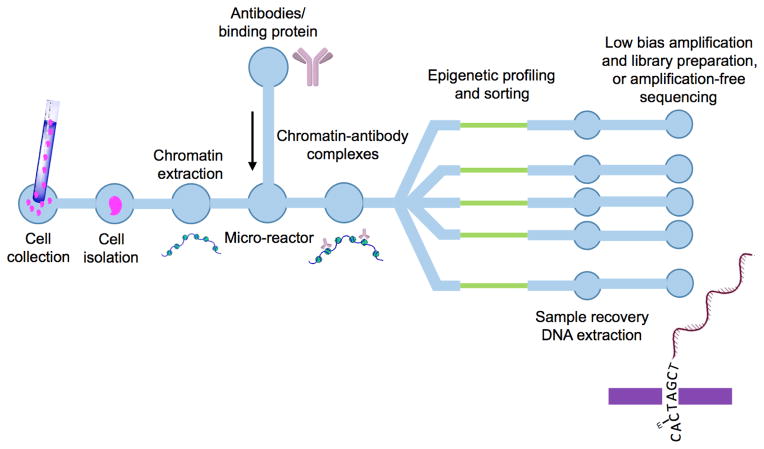
Figure 3. Potential integrated micro-/nano-device architecture for multiplexed epigenomic measurements and amplification-free sequencing from a single cell.
A schematic diagram depicting an integrated device for profiling combinations of epigenomic states from single cells using single molecule methods. Examples of each module of the integrated device were described in the text. From left, isolation of cells for analysis followed by extraction of chromatin from cells [41, 118, 121]; binding of antibodies or other reagents at high concentration in a low volume microreactor to detect epigenomic features [123, 133–135]; removal of unbound antibody can improve throughput of informative chromatin containing complexes; sorting of chromatin carrying various user defined combinations of epigenomic marks [100]; extraction of DNA from sorted chromatin; library preparation after low bias WGA [105, 155–157] followed by sequencing, or amplification free sequencing.