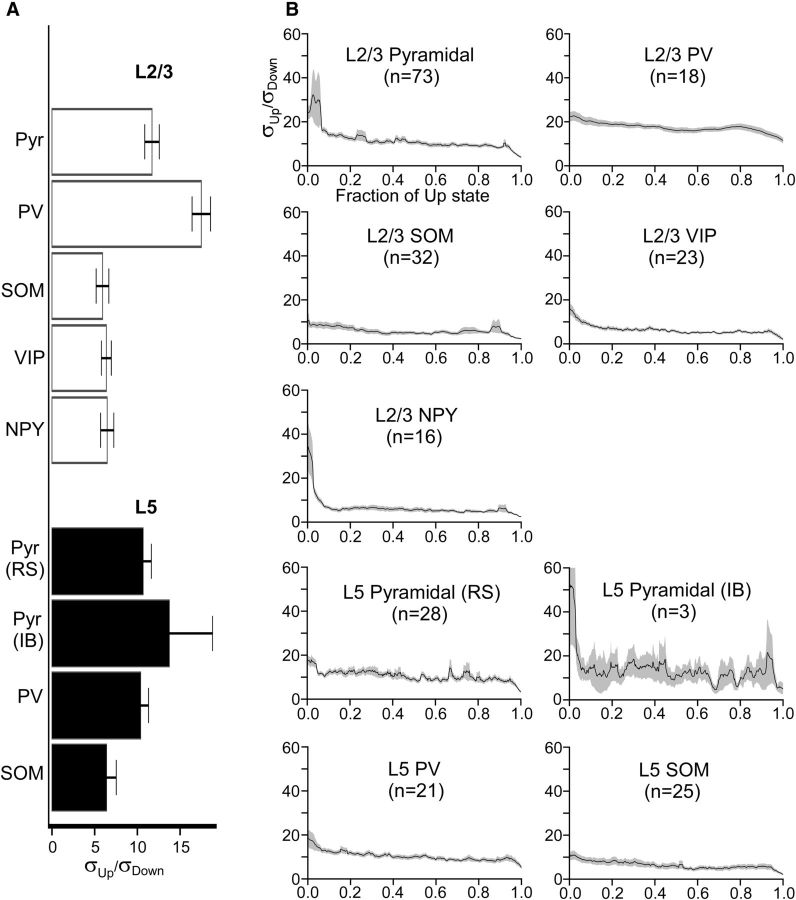
Figure 7.
Membrane potential dynamics of pyramidal cells and interneurons during Up states. A, Mean total membrane potential SDs of pyramidal cells and interneurons. Up-state membrane potential SDs are expressed as multiples of Down-state membrane potential SDs (e.g., a value of σUp/σDown = 5 indicates that the membrane potential SD was 5 times higher during the Up state than during the Down state). Error bars indicate SEM. B, Mean time-dependent SDs of the membrane potential of pyramidal cells and interneurons. SDs are plotted as a function of the fraction of the Up state (i.e., the time axis is normalized from 0 to 1 to average across recordings with different Up-state durations). Shading represents SEM. The following comparisons were significant (Kruskal–Wallis test, Bonferroni correction): σL5 Pyr, RS < σL2/3 PV (p = 0.0018), σL5 Pyr, RS > σL2/3 SOM (0.0030), σL5 Pyr, RS > σL2/3 VIP (0.011), σL2/3 Pyr > σL2/3 PV (3.0 × 10−4), σL2/3 Pyr > σL5 SOM (0.0030), σL2/3 Pyr > σL2/3 SOM (2.9 × 10−4), σL2/3 Pyr > σL2/3 VIP (3.9 × 10−5), σL2/3 Pyr > σL2/3 NPY (0.017), σL5 PV > σL2/3 PV (7.3 × 10−4), σL5 PV > σL2/3 SOM (0.0037), σL5 PV > σL2/3 VIP (0.015), σL2/3 PV > σL5 SOM (2.3 × 10−6), σL2/3 PV > σL2/3 SOM (4.8 × 10−9), σL2/3 PV > σL2/3 VIP (7.0 × 10−10), σL2/3 PV > σL2/3 NPY (1.7 × 10−8).