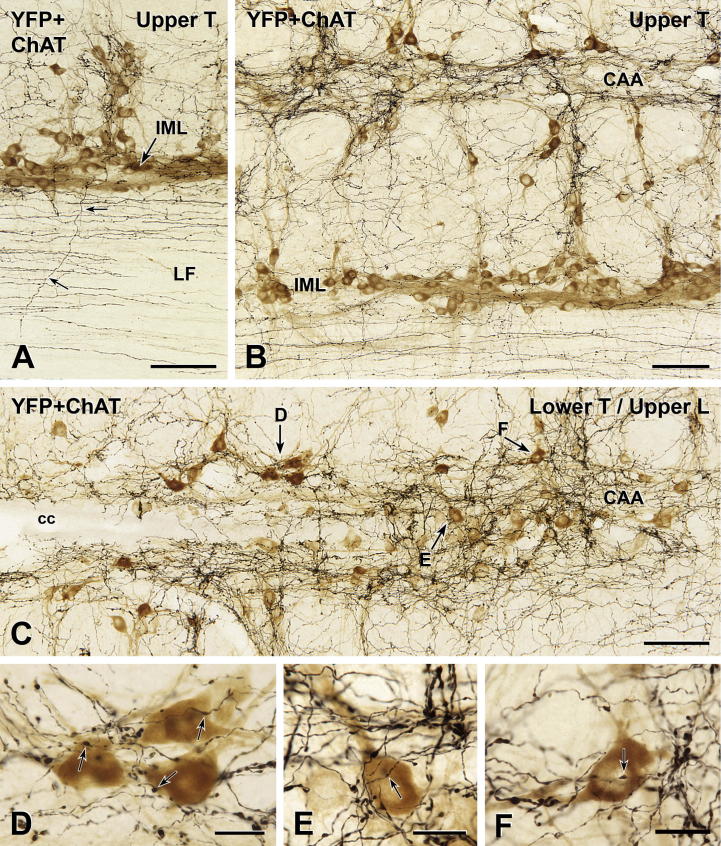
Fig. 5.
YFP-immunoreactive innervation of sympathetic preganglionic neurons (SPN). Two-color immunoperoxidase staining for YFP (black) and ChAT (brown) in horizontal sections through the spinal cord at upper thoracic (Upper T; A and B) and lower thoracic/upper lumbar (Lower T/Upper L; C) levels. At both spinal levels (B and C), black YFP-immunoreactive axons most densely innervate the central autonomic area (CAA), which lies dorsal to the central canal (cc) in lamina X. The intermediolateral cell column (IML) receives a moderately dense black YFP innervation. The lateral funiculus (LF; A and B) contains primarily black YFP-immunoreactive axons of passage that run rostrocaudally and occasional axons that travel mediolaterally (small arrows in A). The neurons indicated by arrows D–F are shown at higher magnification in D–F. Micrographs in montages: A, 3; B, 9; C, 6. (D–F) Black YFP-immunoreactive boutons from close appositions (arrows) on brown ChAT-immunoreactive SPN in the CAA. E, Montage of 2 micrographs. Scale bars: A–C, 100 μm; D–F, 20 μm. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)