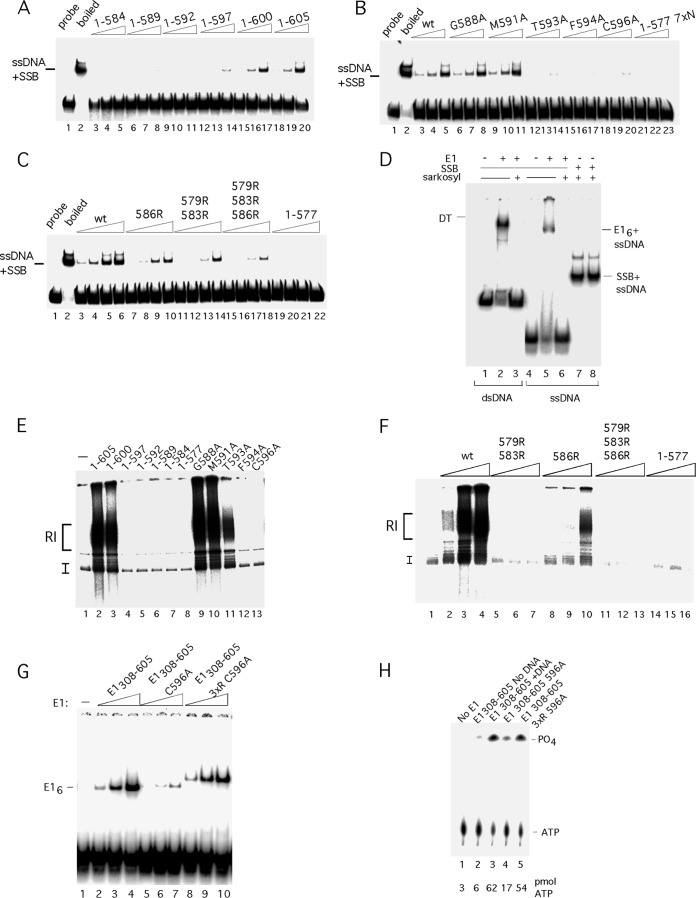
FIG 5.
The C-terminal module is required for unwinding and DNA replication in vitro. (A) The 84-bp ori probe was incubated with three levels (2.5, 5, and 10 ng) of E11–584, E11–589, E11–592, E11–597, E11–600, and E11–605 in the presence of ATP and E. coli SSB and analyzed by EMSA. ssDNA + SSB complexes are indicated. (B) The 84-bp ori probe was incubated with three levels (2.5, 5, and 10 ng) of E11–605, E11–605 G588A, E11–605 M591A, E11–605 T593A, E11–605 F594A, E11–605 C596A, and E11–577 7×N in the presence of ATP and E. coli SSB and analyzed by EMSA. (C) The 84-bp ori probe was incubated with four levels (2.5, 5, 10 and 20 ng) of E11–605, E11–605 586R, E11–605 579R/583R, E11–605 579R/583R/586R, and E11–577 in the presence of ATP and E. coli SSB and analyzed by EMSA. (D) Low levels of Sarkosyl disrupt E1 complexes with ssDNA and dsDNA but do not affect complexes between E. coli SSB and ssDNA. The double-stranded 84-bp ori probe was incubated with E1 in the presence of ADP (lanes 2 and 3). Immediately before loading onto an EMSA gel, one sample (lane 3) was treated with 0.1% Sarkosyl. The ssDNA probe was incubated with E1 in the presence of ADP (lanes 5 and 6). Immediately before loading onto an EMSA gel, one sample (lane 6) was treated with 0.1% Sarkosyl. The ssDNA probe was incubated with E. coli SSB (lanes 7 and 8). Immediately prior to loading onto the EMSA gel, one sample (lane 8) was treated with 0.1% Sarkosyl. (E) Deletions and point mutations in the acidic region and C tail were expressed and purified from E. coli and tested for DNA replication in vitro as described in Materials and Methods. Two hundred nanograms of each mutant protein was incubated in replication extract in the presence of [α-32P]dCTP and analyzed by agarose gel electrophoresis. (F) The arginine substitutions in the acidic region were tested for DNA replication in vitro. Three quantities (100, 200, and 400 ng) of wt E1 and the E1 579R/583R, 586R, 579R/583R/586R mutants and E11–577 were used in cell-free replication reactions in the presence of [α-32P]dCTP and analyzed by agarose gel electrophoresis. (G) Inactivation of the acidic region in the context of the E1308–605 C596A restores E1 hexamer formation and ATPase activity to wt levels. Mutants in the C-terminal module were tested for hexamer formation in the context of E1308–605 using an ssDNA probe. Two, 4, and 8 ng each of the proteins E1308–605, E1308–605 C596A, and E1308–605 C596A D579R/D573RE586R were incubated with a 41-mer ssDNA probe (∼2 fmol) in the presence of ADP and tested for hexamer formation by EMSA. The migration of the E1 hexamer is indicated. The altered mobility of the complexes formed with E1308–605 C596A D579R/D573RE586R is caused by the E586R substitution. (H) Mutants in the C-terminal module in the context of E1308–605 were tested for ATPase activity. The proteins E1308–605, E1308–605 C596A, andE1308–605 C596A D579R/D573RE586R were incubated with [γ-32P]ATP and ssDNA, unless otherwise indicated, and tested for ATPase activity as described in Materials and Methods. The migration of ATP and free phosphate is indicated, and the level of hydrolyzed ATP is shown below the lanes.