FIG 2.
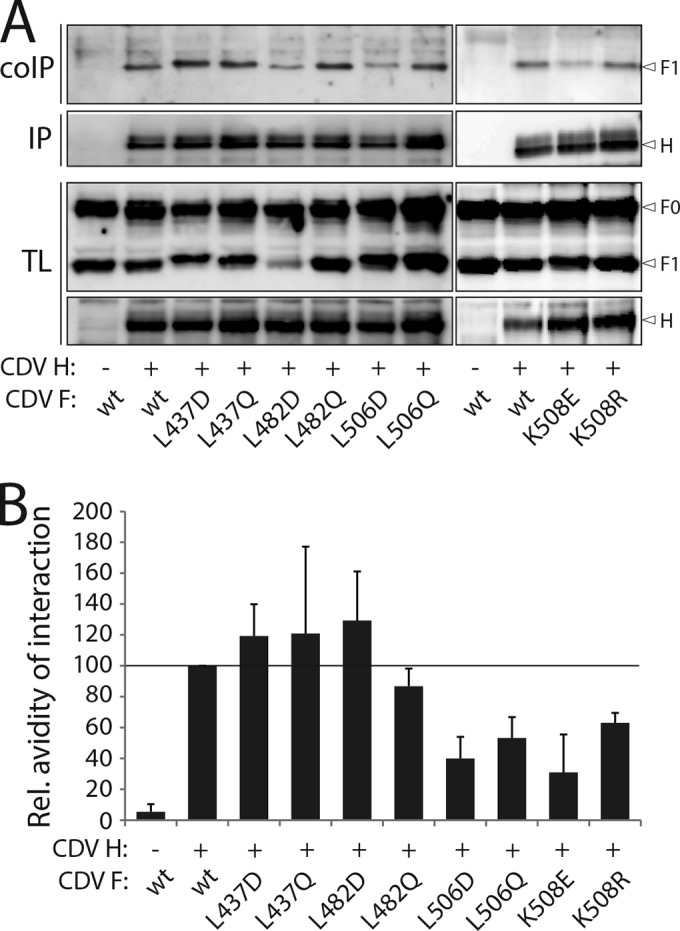
Substitution of critical hydrophobic residues in F with polar or charged amino acids impaired H binding activity. (A) Cell surface assessment of H interaction with cleaved F proteins. To stabilize H-F complexes, transfected Vero cells were treated with the non-membrane-permeable cross-linker dithiobis(sulfosuccinimidylpropionate) (DTSSP) and subsequently lysed with radioimmunoprecipitation assay (RIPA) buffer. Complexes were then immunoprecipitated (IP) with anti-CDV H MAbs 2267 and 3734 (40) and protein G-Sepharose bead treatment. Proteins were boiled and subjected to immunoblotting using a polyclonal anti-CDV-F antibody (41) to detect F antigenic materials (coIP). CoIP F proteins were detected in comparison with F proteins present in cell lysates prior to IP by immunoblotting using the same anti-F antibody (TL, total lysate; F0, uncleaved F protein; F1, cleaved membrane-anchored F subunit). (B) Semiquantitative assessment of F/H avidity of interactions. To quantify the avidities of F1-H interactions, the signals in each F1 and H band were quantified using the AIDA software package. The avidity of F1-H interactions is represented by the ratio of the amount of coimmunoprecipitated (coIP) F1 over the product of F1 in the cell lysates divided by the ratio of the amount of immunoprecipitated H over the product of H in the cell lysate [(coIP F1/TL F1)/(IP H/TL H)]. Subsequently, all ratios were normalized to the ratio of the wild-type F-H interactions, set to 100%. Values are averages of results from at least three independent experiments.
