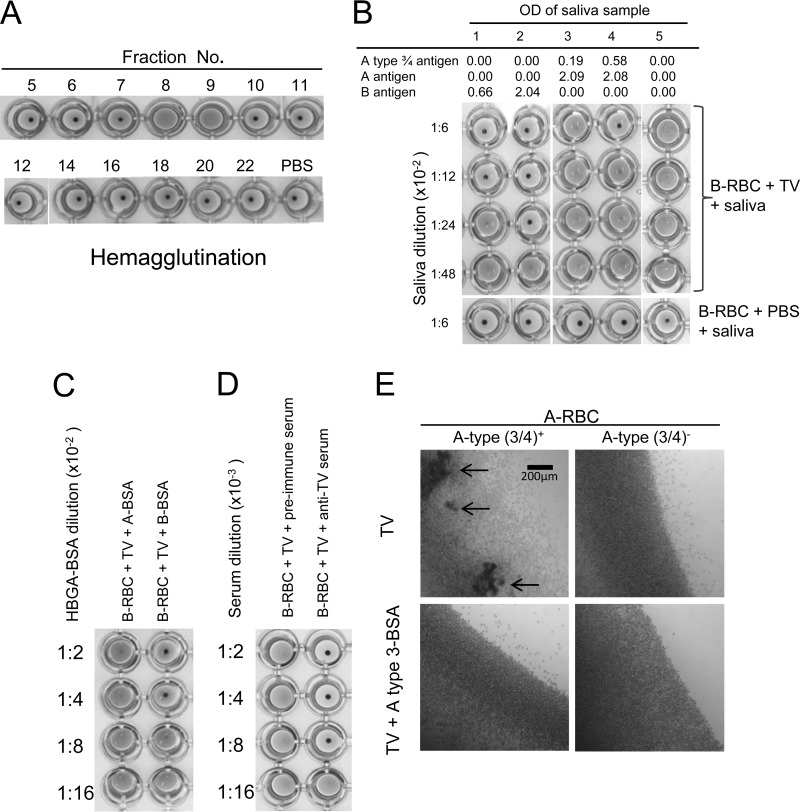
FIG 4.
Hemagglutination of human red blood cells (RBCs) by TV. (A) Hemagglutination of type B human RBCs by TVs from CsCl gradient fractions. Only fractions 8 and 9 contained intact TVs, which was determined by electron microscopy followed by ELISA and detection by PCR. (B) Inhibition of TV-induced hemagglutination by saliva containing A type 3/4 and B antigens. Strong inhibition by the type B saliva (saliva samples 1 and 2) which correlated with the salivary B antigens was observed. Inhibition was also observed for the A type 3/4-positive saliva (saliva samples 3 and 4), but inhibition was not seen for the type O saliva (saliva sample 5). (C and D) Inhibition of TV induced hemagglutination by type B oligosaccharide and by antibody to TV. (E) Inhibition of TV induced hemagglutination by A type 3 oligosaccharide using flat-bottom plates followed by reading of the results under a microscope. Weak agglutination of A type 3/4-positive RBCs developed, and the hemagglutination could be blocked by a synthetic A type 3 oligosaccharide conjugate. Arrows indicate typical agglutinations of RBCs.