Figure 4.
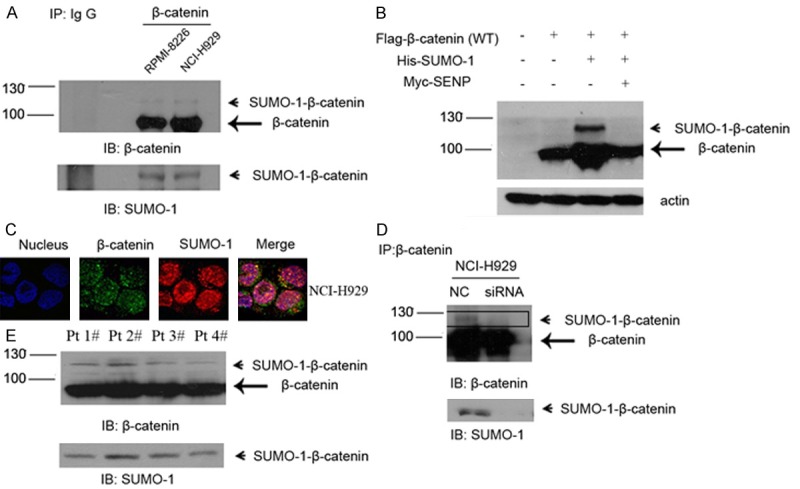
Endogenous β-catenin is modified by SUMO-1 in myeloma cells. A. Myeloma cells RPMI-8226 and NCI-H929 were harvested under denaturing conditions as described under “Experimental Procedures” and immunoprecipitated with anti-β–catenin rabbit antibody or IgG as a control. The immunoprecipitates (IP) were resolved by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted with anti-β-catenin and anti-SUMO-1 antibodies respectively. SUMOylated β-catenin and non-SUMOylated β-catenin were indicated by arrow head and arrow, respectively. B. NCI-H929 was transfected with Flag-tagged β-catenin or together with His-tagged SUMO-1 or Myc-tagged SENP1, after 48 hours, cells were harvested and then subjected to western blot with anti-Flag antibody. C. Endogenous β-catenin co-localized with SUMO-1. Myeloma cells NCI-H929 were fixed and stained with anti-β-catenin mouse antibody (green) and anti-SUMO-1 rabbit antibody (red). DNA was stained with DAPI. The images were taken by confocal microscopy as described under “Experimental Procedures”. D. After transfection of negative control and/or SUMO-1 siRNA for 48 hours, whole cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-β-catenin antibody. The immunoprecipitates (IP) were resolved by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted with anti-β-catenin and anti-SUMO-1 respectively. SUMOylated β-catenin was indicated by arrow head. E. Bone marrow samples were isolated from myeloma patients. Total lysate was prepared from 5 × 106 cells in each sample and immunoprecipitated with anti-β–catenin rabbit antibody as mentioned above. The immunoprecipitates (IP) were resolved by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted with anti-β-catenin and anti-SUMO-1 antibodies respectively. SUMOylated β-catenin and non-SUMOylated β-catenin were indicated by arrow head and arrow, respectively.
