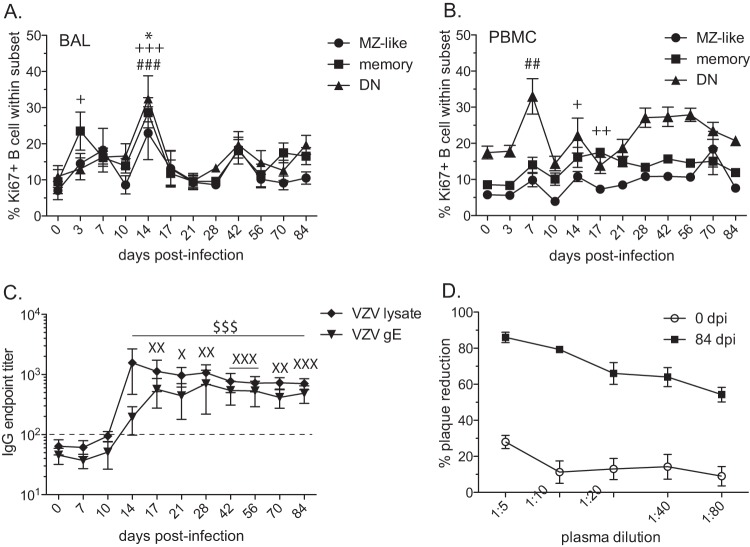
FIG 2.
VZV-infected rhesus macaques develop VZV-specific B cell responses. (A, B) Percentages of proliferating marginal zone-like (MZ-like), memory (M), and double-negative (DN) B cells in BAL samples (A) and PBMC (B) were measured by flow cytometry based on the expression of Ki67. Ki67+, Ki76 positive. (C) Endpoint titers of VZV-specific IgG antibody to VZV lysate or VZV gE were measured by standard ELISA. (D) Neutralizing potentials of anti-VZV antibodies were assessed using plaque reduction assay on days 0 and 84 postinfection. Dashed line indicates background level. The results shown are the average values ± SEM. Statistical analysis was performed using one-way repeated-measures ANOVA with Dunnett's posttest to assess differences between preinfection and postinfection values (P < 0.05: *, MZ-like; +, memory; X, VZV gE; P < 0.01: ++, memory; ##, DN; XX, VZV gE; P < 0.001: +++, memory; ###, DN; XXX, VZV gE; $$$, VZV lysate).