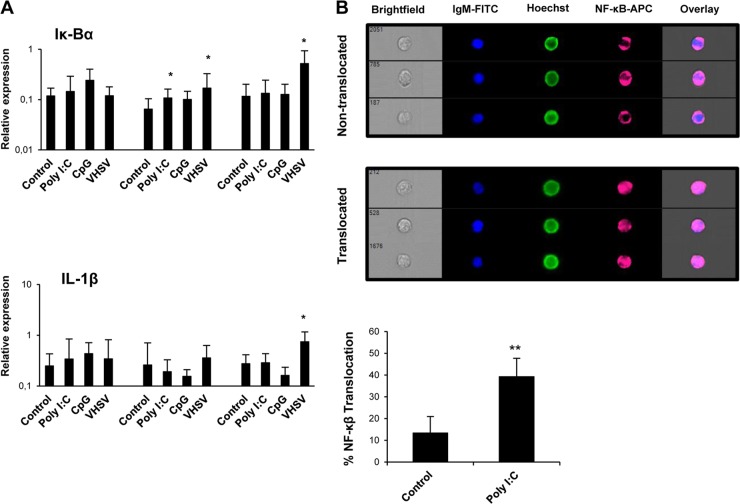
FIG 7.
VHSV and poly(I·C) activate NF-κB in IgM+ B cells. (A) Splenocytes were stimulated as described in the legend of Fig. 1. IgM+ B cells were then sorted, and RNA was extracted for the evaluation of IκBα and IL-1β transcription levels by real-time PCR (n = 7). Data are shown as mean gene expression levels relative to the expression level of an endogenous control (EF-1α) ± standard deviations. *, P < 0.05. (B) Translocation of NF-κB to the nucleus in trout IgM+ splenocytes following poly(I·C) stimulation. Trout splenocytes were stimulated with poly(I·C) or with medium alone for 24 h at 20°C. NF-κB translocation in IgM+ cells was determined following staining with anti-p65 and anti-trout IgM MAbs. Hoechst stain was used to visualize cell nuclei. Percentages of NF-κB translocation in trout IgM+ cells are represented together with representative images of positive nuclear translocation (Translocated) and negative translocation (Nontranslocated) using an ImageStream MKII imaging flow cytometer (Amnis). Data were collected from five different trout (n = 5) over three independent experiments. **, P < 0.05 (based on comparisons with medium-alone controls).