FIG 1.
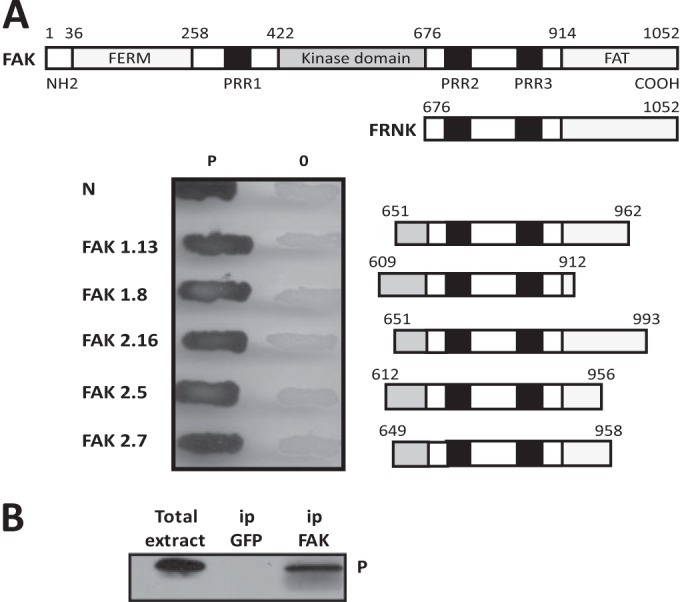
The RABV P protein binds FAK. (A) Mapping of the P protein binding domain within FAK by two-hybrid screen. The major domains of FAK (the FERM, kinase, and FAT domains) and the PRR are shown. FRNK is transcribed from a second promoter within the FAK gene and comprises the FAT domain and 2 PRR (top). Several pGAD clones containing different C-terminal fragments of FAK fused to the Gal4 AD were isolated during the two-hybrid screen. Yeast cells (strain L40) were cotransformed with these pGAD plasmids and the pLex plasmid encoding P fused to the DB or empty pLex plasmid (0). The P-FAK interaction is indicated by the appearance of blue colonies in the presence of X-Gal (bottom). P-N interaction was also analyzed. (B) Detection of P-FAK interaction in infected cells. HEK293T cells were transfected with a plasmid expressing FAK. At 24 h posttransfection, the cells were infected with wild-type CVS at an MOI of 3 PFU/cell. At 24 h after infection, cells were harvested and lysed. The cell lysate was incubated with a rabbit polyclonal anti-FAK or anti-GFP antibody. Immune complexes were precipitated (ip) by incubation with protein A-Sepharose and analyzed by Western immunoblotting with mouse monoclonal anti-P antibody. In the left portion of the blot, total cellular extracts were also analyzed.
