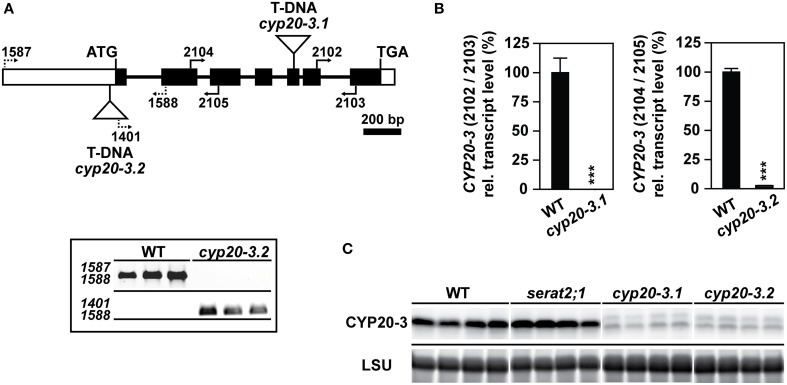
Figure 1.
Identification, molecular characterization and gene expression analysis of cyp20-3 mutant lines. (A) Gene model of the Arabidopsis thaliana gene CYP20-3 (AT3G62030). Exons and introns are illustrated as black boxes and thin lines, respectively. White boxes represent 5′- and 3′-UTRs. Triangles define the two T-DNA insertions of cyp20-3.1 and cyp20-3.2, respectively. Black arrows and numbering indicate the positions of used primers. Molecular verification of cyp20-3.2 by PCR using specific primer combinations for the wild type (WT) allele (upper panel) and mutant allele (lower panel). (B) CYP20-3 gene expression levels by qRT-PCR with cyp20-3.1 and cyp20-3.2 cDNA and indicated primer combinations. WT transcript levels were set to 100%. Statistically significant differences are indicated as asterisks (***p ≤ 0.001; Student's t-test). Results represent means ± SE (n = 3). (C) Immunological detection of CYP20-3 using a polyclonal antibody against Arabidopsis CYP20-3 in leaf protein extracts of WT, serat2;1, cyp20-3.1 and cyp20-3.2 plants (four lanes each) grown under control conditions. Staining intensities of the large subunit of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase (LSU) protein in the same samples confirm equal loading in the individual lanes.