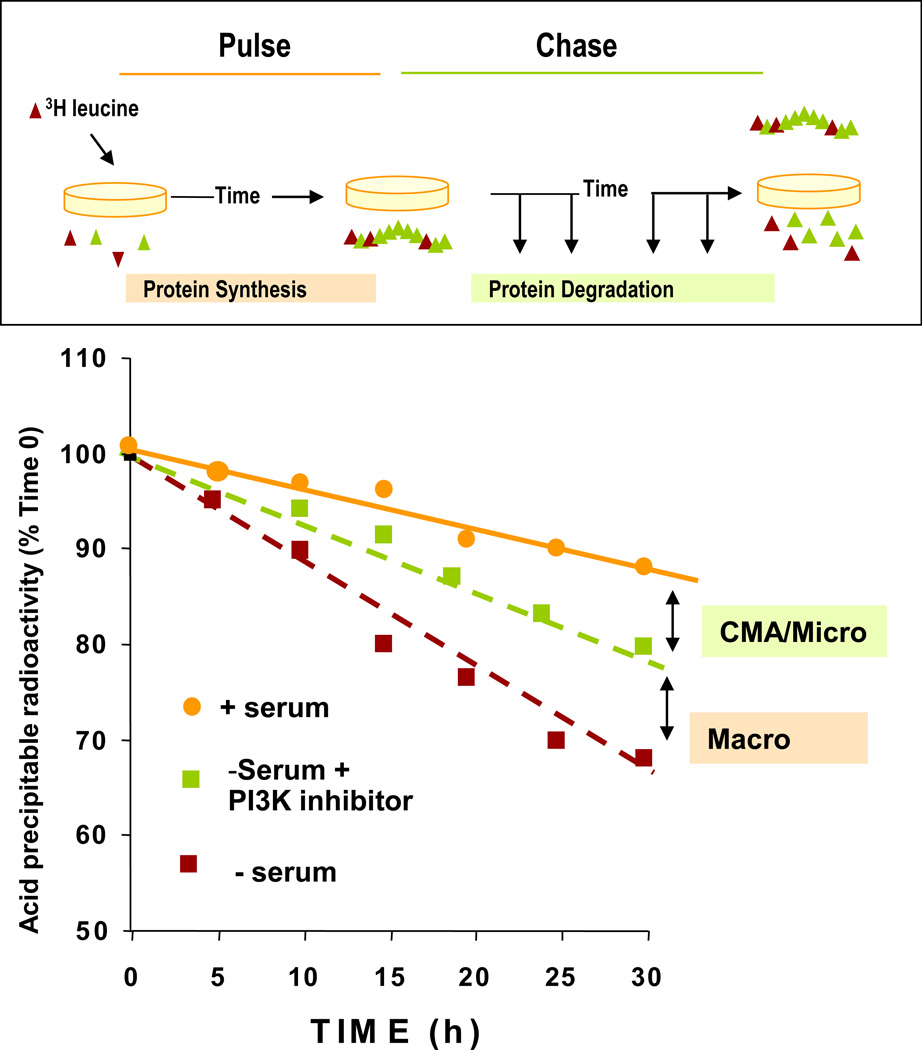
Figure 1. Measurement of long-lived protein degradation.
Top: Confluent cells in culture are incubated with a radiolabeled amino acid for 48 h and after extensive washing the amount of acid-soluble radioactivity (amino acids and small peptides) released into the medium at different times is determined. Bottom: Typical example of rates of degradation of long-lived proteins in cultured cells due to CMA, micro- or macroautophagy. CMA activity is calculated as the increase in protein degradation during serum deprivation sensitive to lysosomal protease inhibition and insensitive to the effect of PI3-K type III inhibitors.