FIG 1.
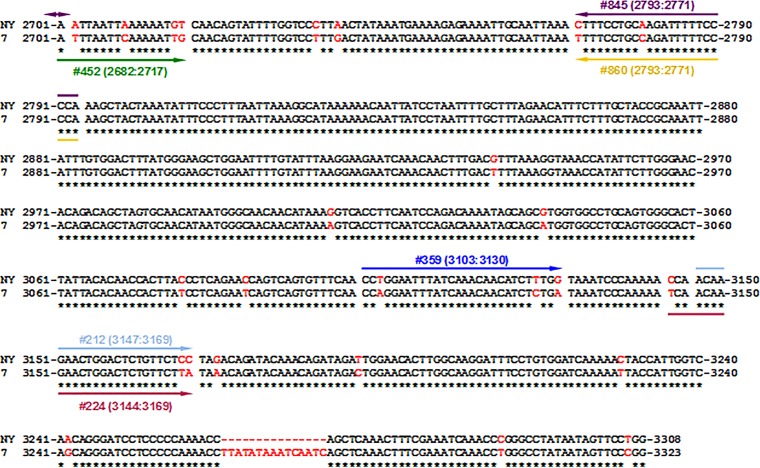
Alignment of the full-genome consensus sequences of the strains WHVNY and WHV7. As described in Materials and Methods, the rcDNA of WHVNY and WHV7 was isolated from the serum samples of monoinfected woodchucks. Eight full-genome molecular clones for each WHV strain were generated using a strategy based on the method described by Gunther et al. (34, 35). Using the molecular clones, the consensus sequences for WHVNY and WHVN7 were obtained using MacVector 11.1.1 software. The alignment of the consensus sequences generated using ClustalW2 software (http://www.ebi.ac.uk/Tools/msa/clustalw2/) is shown. The sequence of WHVNY is shown on the top row, while the sequence of WHV7 is on the bottom row. Identical nucleotides are indicated by asterisks underneath. The nonidentical nucleotides are shown in red. The genome of WHVNY contains a 15-nucleotide-long deletion which corresponds to the positions 3264 to 3278 of the WHV7 genome. The positions of primers (each primer is shown as a line with a single arrow) and probes (each probe is shown as a line with two arrows) used for the strain-specific conventional PCR and qPCR assays are indicated relative to the alignment. In the first round of nested PCR to detect serum WHVNY rcDNA, primers 359 (3103:3130) and 357 (1655:1636) (blue) were used. For the second round of PCR, primers 212 (3147:3169) and 195 (1223:1203) (light blue) were employed. For WHV7 rcDNA detection, primers 452 (2682:2717) and 218 (1412:1392) (green) were used for the first round of PCR. The second round of amplification was carried out using primers 224 (3144:3169) and 217 (1223:1203) (light purple). For WHVNY RNA detection, the cDNA synthesis was carried out using WHVNY-specific primer 357. Amplification was carried out by seminested PCR using primers 511 (141:161) and 505 (1410:1392) (in some cases, primer 357 was used instead of 505 [see Materials and Methods]) for the first round (red). The second round of amplification was carried out using primers 511 and 195. WHV7 cDNA synthesis was performed using WHV7-specific primer 218. Amplification was carried out by the same nested PCR method as that used for the rcDNA detection, employing primers 452 and 218 for the first round of amplification and primers 224 and 217 for the second round of PCR. The quantification of serum rcDNA and replicative intermediate DNA (RI-DNA) of WHVNY in tissue samples was done by qPCR using primers 844 (2625:2651) and 845 (2793:2771) and probe 846 (2670:2701) (purple). For WHV7 rcDNA and RI-DNA quantification, primers 859 (2625:2651) and 860 (2793:2771) and probe 861 (2656:2685) (yellow) were used. For the quantification of WHVNY cccDNA in tissue samples, a preamplification step (conventional PCR) was carried out using primers 756 (1437:1453) and 638 (2166:2143) (orange). Then, in the next step, qPCR was performed using primers 782 (1581:1596) and 783 (1956:1936) and probe 784 (1623:1646) (beige). The quantification of WHV7 cccDNA was carried out using primers 862 (1581:1596) and 783 and probe 864 (1623:1646) (black).