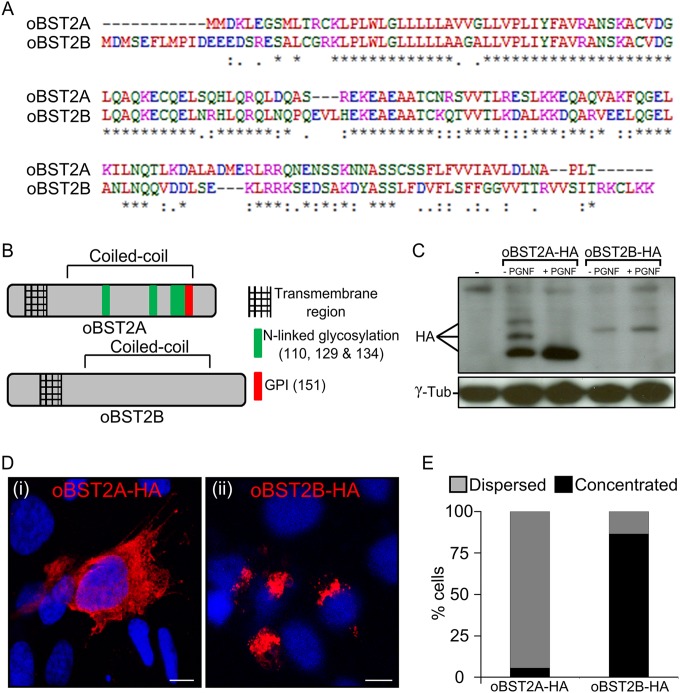
FIG 1.
oBST2A and -2B have different biological features. (A) Alignment of the amino acid sequences of the ovine BST2 proteins (oBST2A and -2B). An asterisk (*) indicates an identical amino acid, a period (.) indicates weak similarity, and a colon (:) indicates strong similarity. (B) Schematic diagram illustrating the main structural features and predicted posttranslational modifications of oBST2A and -2B. (C) HEK-293T cells were transiently transfected with expression plasmids for oBST2A-HA or -2B-HA. Cell lysates were harvested and incubated in the presence and absence of PNGase F overnight. Proteins were then separated by SDS-PAGE and visualized by Western blotting using an HA antibody. γ-Tubulin was used as a sample-loading control. (D) Confocal microscopy images of oBST2A-HA and oBST2B-HA in transiently transfected CPT-Tert cells display two different patterns: (i) dispersed within the cytoplasm and cell membrane and (ii) concentrated in a perinuclear region. Scale bars in both panels represent 10 μm. (E) Graph representing the number (%) of cells in which oBST2A-HA- and oBST2B-HA-staining patterns were counted as dispersed or concentrated. At least 75 cells in random fields from two independent experiments were scored.