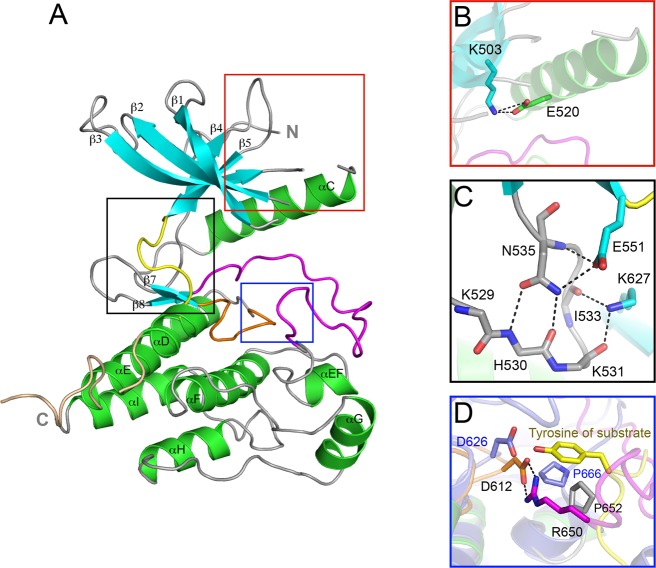
Figure 1.
The crystal structure of wild-type FGFR4 kinase. (A) Ribbon diagram of the wild-type FGFR4K structure. β strands and α helices are colored cyan and green, respectively. The A-loop, catalytic loop, kinase insert, and kinase hinge are colored magenta, orange, wheat, and yellow, respectively. (B) Close-up view of the N-lobe showing formation of the catalytically critical salt bridge between K503 and E520. (C) Close-up view of the molecular brake at the kinase hinge region. (D) Close-up view of the active site of FGFR4KWT and activated FGFR2K (in slate) complexed with peptide (in yellow sticks) following superimposition of these two structures. Note that bidentate hydrogen bonds between R650 and D612 (the general base) block the access of substrate tyrosine into the active site of FGFR4K. The side chain of R650 in the FGFR4K structure occupies roughly the same space as the substrate tyrosine in the FGFR2K–peptide complex structure. In all figures, side chains of selected residues are shown as sticks, and atom colorings are as follows: oxygens in red, nitrogens in blue, and coloring of carbons follow the coloring scheme of the specific region of the kinase from which they derive. The hydrogen bonds are shown as black dashed lines.