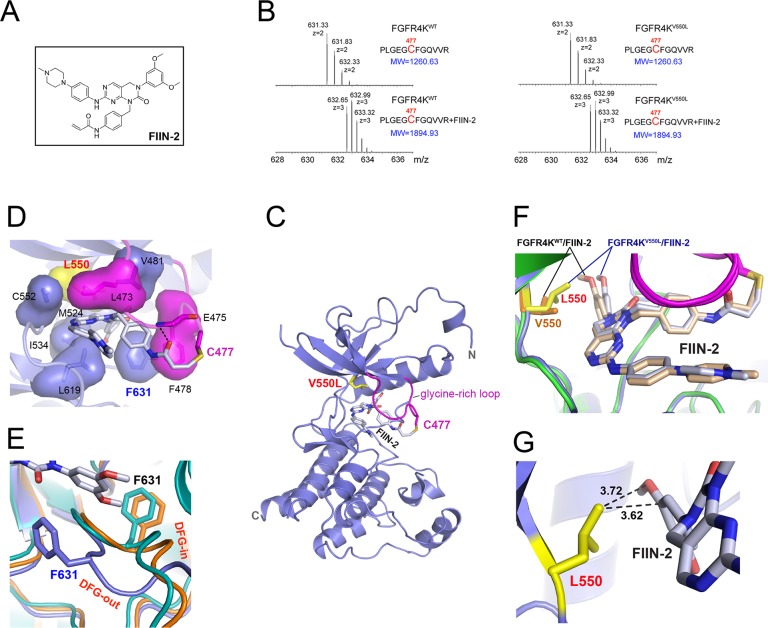
Figure 5.
Structural basis for the inhibition of FGFR4KV550L gate-keeper mutant by FIIN-2. (A) The chemical structure of FIIN-2. (B) The LC-MS/MS spectra of the kinase peptide (Pro42-Arg53) from FGFR4KWT and FGFR4KV550L with and without FIIN-2. The reacting Cys477 from the glycine-rich loop of the kinase is highlighted in red color. (C) Ribbon diagram of the FGFR4KV550L–FIIN-2 cocrystal structure. (D) The close-up view of the main interactions between FGFR4KV550L and FIIN-2. The hydrogen bonds are indicated as black dashed lines, and the hydrophobic interactions are shown as surface. (E) Close-up view of the DFG motif conformation in the FGFR4KWT (in orange), FGFR4KV550L (in teal), and FGFR4KV550L–FIIN-2 (in blue) structures following superimposition of the three structures. Note that FIIN-2 also binds to the ATP-binding site of FGFR4K in DFG-out mode. The phenylalanines in the DFG region of FGFR4KWT, FGFR4KV550L, and the FGFR4KV550L–FIIN-2 complex are rendered as orange, teal, and blue sticks and labeled in black and blue, respectively. (F) Superimposition of the FGFR4KWT–FIIN-2 complex structure onto the FGFR4KV550L–FIIN-2 structure. Note that rotational freedom around the single bond linking the scaffold and dimethoxyphenyl of FIIN-2 allows for small structural adjustments to bypass any potential steric clash with the bulkier side chain of L550. The V550 in FGFR4KWT and L550 in FGFR4KV550L are shown in orange and yellow sticks, and labeled in orange and red, respectively. (G) The distances between L550 of the FGFR4KV550L gate-keeper mutant and FIIN-2 are shown as dashed lines and labeled in a black color. In all of the structures, the FIIN-2 is rendered as sticks and labeled in black.