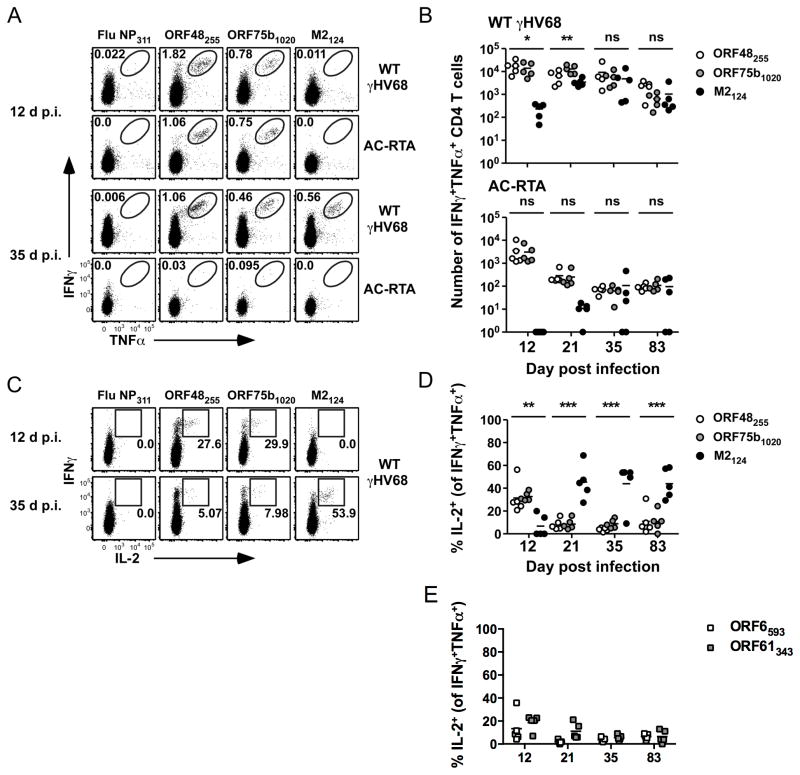
Figure 3. Epitope-specific CD4 T cells are polyfunctional.
(A) Representative dot plots showing IFNγ and TNFα production by lung CD4 T cells at 12 or 35 d after WT γHV68 or AC-RTA infection. Numbers in the plots indicate the percent of CD4 T cells in the gate. (B) The number of IFNγ+TNFα+ CD4 T cells in the lungs over time after WT γHV68 or AC-RTA infection (n=5, representative of 4 experiments; ns, not significant; *P≤0.05; **P≤0.01; one-way ANOVA). (C) Representative dot plots showing IFNγ and IL-2 production by CD4 T cells at 12 days or 35 days after WT γHV68 infection. Numbers in the plots indicate the percent of IFNγ+TNFα+ CD4 T cells expressing IL-2. (D, E) The percent of IFNγ+TNFα+ CD4 T cells that are IL-2+ in the lungs specific for the indicated antigens over time after WT γHV68 infection (n=5, representative of 4 experiments; **P≤0.01; ***P≤0.001; one-way ANOVA).