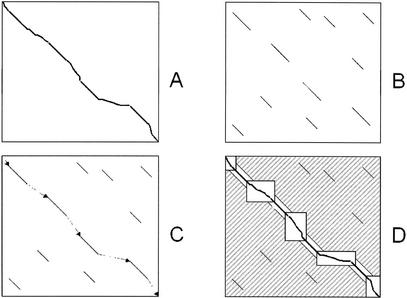
Figure 1.
The LAGAN algorithm. (A) A global alignment between two sequences is a path between the top-left and the bottom-right corner of their alignment matrix. (B) LAGAN first finds all local alignments between the two sequences. (C) LAGAN computes a maximal-scoring ordered subset of the alignments, the anchors, and puts together a rough global map. (D) LAGAN limits the search for an optimal alignment to the area included in the boxes and around the anchors, and computes the optimal Needleman-Wunsch alignment limited to that area. LAGAN uses memory proportional to the area of the largest box plus the memory to hold the optimal alignment.