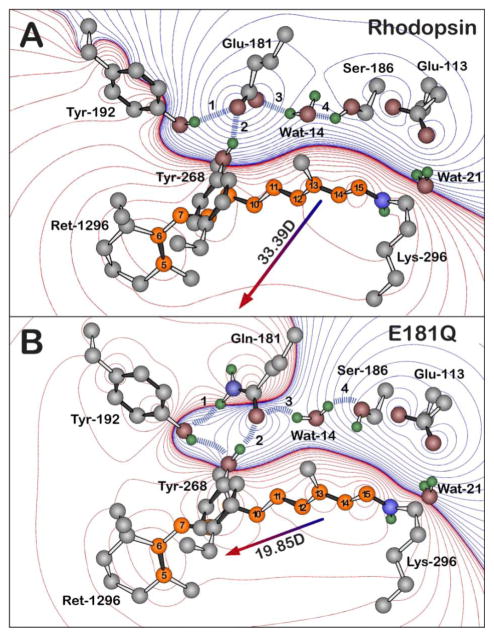
Figure 8.
The hydrogen bonding network of the negatively charged Glu-181 residue of native rhodopsin (A) and of the Gln-181 residue of E181Q (B), both during the Lumi photointermediate. The blue dashed lines and the labels 1–4 highlight the key hydrogen-bonding network between residue 181, Ser-186, Tyr-192, Tyr-268, and Wat-14, which is perturbed upon the glutamine substitution. The Lumi structure (A) is based off of the 2HPY crystal structure [57] and a relaxed conformation of the Lumi photointermediate of E181Q (B) was obtained by minimizing the crystal structure with Gln-181. Polyene atoms of retinal (Ret-1296) are indicated in orange, and the numbering system shown here is used in the text. The water molecules are labeled using the Protein Data Bank (PDB) numbers minus 2000. All hydrogen atoms were included in the calculations and were optimized by using B3LYP/6-31G(d) methods, although only polar hydrogens are shown in the figure. Red and blue contours indicate regions of increased positive and negative charge, respectively. The contours are drawn by using the following first-order electrostatic energies: 0 (black), ± 0.282, ± 2.26, ± 7.63, ± 18, ± 35.3, ± 61, ± 96.9, ± 144, ± 206, ± 282, ± 376, ± 488, ± 621, ± 755 kJ/mol.