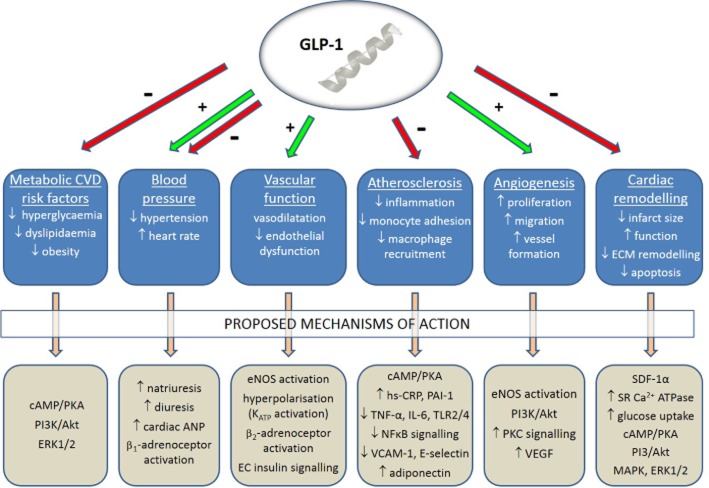
Figure 2.
Proposed mechanisms underlying the reported cardiovascular actions of GLP-1. Although it is well established that GLP-1 exerts several beneficial effects on the CVS relevant to diabetes, such as reduction of metabolic CVD risk factors, BP modulation, improved vascular function, decreased atherosclerosis, promotion of angiogenesis and attenuation of adverse cardiac remodelling, the precise mechanisms are yet to be established, although several pathways have been proposed which are the focus of further investigation. EC, endothelial cell; ECM, extracellular matrix; SDF, stromal cell-derived factor 1α; SR, sarcoplasmic reticulum.