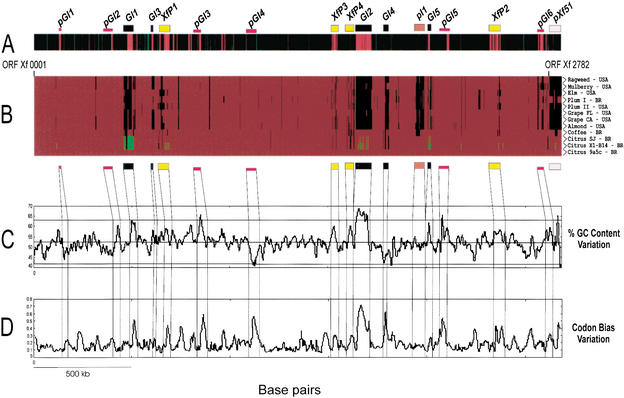
Figure 1.
A comparative and functional analysis of X. fastidiosa genomes. (A) The relative chromosomal position of genes that showed transcription upregulation in PW (red bars) and XDM (green bars) media. Most PW-overexpressed genes are located in clusters that coincide with prophages or GI regions. (B) The genomic profiles among 12 Xf isolates obtained from different hosts and disparate geographical origins. DNA from these isolates was labeled with Cy5-dCTP and submitted to competitive microarray hybridization with Cy3-labeled DNA from Xf strain 9a5c. ORFs were categorized as common to the two strains, exclusive to Xf strain 9a5c, or duplicated in the test strain, depending on the specific Cy5/Cy3 ratio. The figure shows the presence/absence of ∼2200 ORFs from Xf strain 9a5c across the genome of all tested strains. A red bar indicates the presence of a gene, a black bar, absence of the gene, and duplicated sequences are represented by a green bar. (C,D) The CG content and codon bias variations in strain 9a5c, respectively. The figure also indicates the relative positions of five genomic islands (GI1–GI5), six putative GIs (pGI1–pGI6), four integrated prophages (XfP1–XfP4), one plasmid integration region (pI1), and pXf51 plasmid, identified in the genome of Xf strain 9a5c.