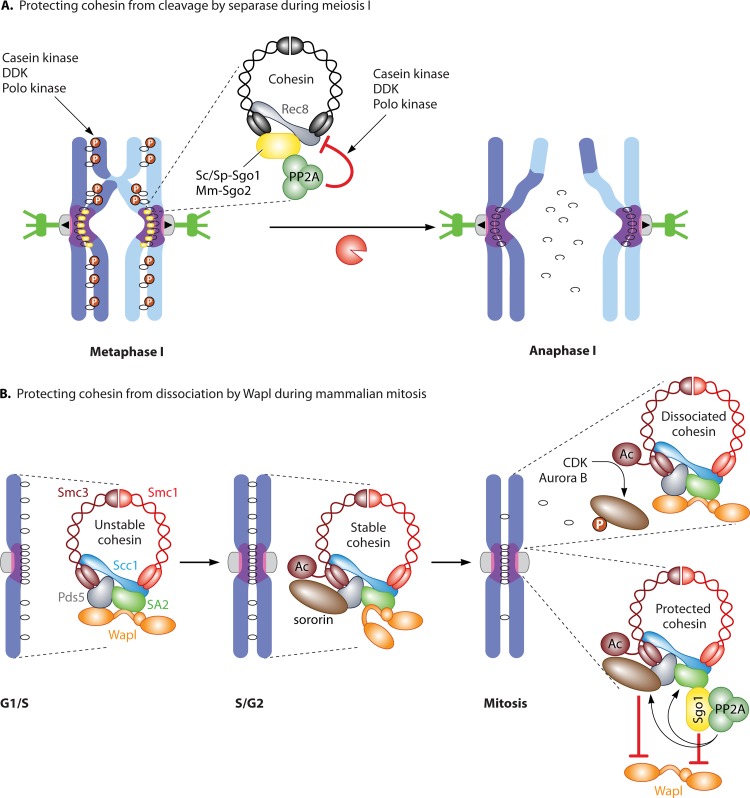
FIG 3.
Protection of cohesin by shugoshins. (A) Mechanism of protecting pericentromeric cohesin from cleavage by separase during meiosis I. Shugoshin recruits PP2A, which prevents Rec8 phosphorylation, making it a poor substrate for separase-dependent cleavage. DDK, Dbf4-dependent kinase. (B) Mechanism of protecting pericentromeric cohesin from dissociation by Wapl during mammalian mitosis. In G1, Wapl can associate with cohesin and make it stable. After S phase, Eco1-dependent acetylation stabilizes cohesin in mammals by associating with sororin, which counteracts Wapl activity. During mitosis, CDK and Aurora B phosphorylate sororin, leading to its release from cohesin and making it susceptible to Wapl. At the pericentromere, shugoshin-PP2A protects cohesin from Wapl activity in two ways: preventing sororin phosphorylation and blocking Wapl binding to SA2.