FIG 5.
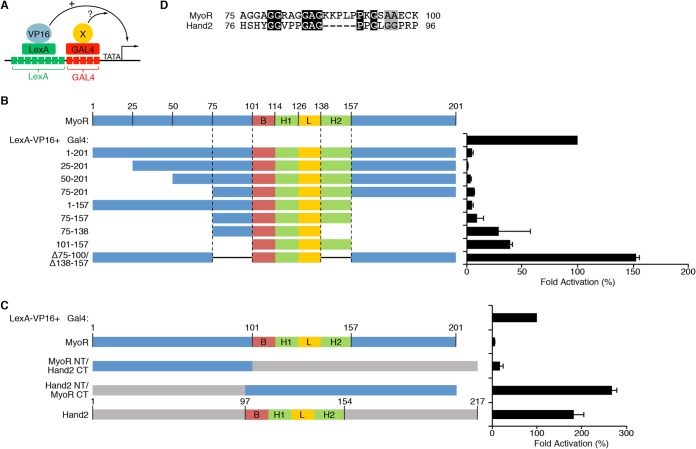
MyoR requires two nonequivalent repression domains to inhibit transcription. (A) Diagram depiction of the trans-repression assay system used for these experiments. The system utilizes a synthetic reporter construct containing eight LexA binding sites adjacent to five Gal4 binding sites. The LexA DNA-binding domain is fused with the HSV VP16 transactivation domain to mediate potent transcriptional activation. Candidate repressors are fused to the Gal4 DNA-binding domain and assessed for inhibitory activity in transient-transfection experiments. (B) A total of 100 ng of Lex8-Gal5-Luc was cotransfected with 100 ng of LexA-VP16 and 200 ng of the indicated Gal4-MyoR deletion construct. Also, 10 ng of CMV-lacZ was transfected for normalization purposes. The data are represented as the fold activation compared to LexA-VP16 alone (100%). N-terminal deletion to amino acid 75 or C-terminal deletion to residue 157 does not impair the ability of Gal4-MyoR to repress transcription by LexA-VP16. C-terminal deletion to residue 138 or N-terminal deletion to residue 100 partially impairs Gal4-MyoR repression. However, deletion of both putative repression domains (75-100 and 138-157) completely eliminates the ability of Gal4-MyoR to inhibit LexA-VP16-dependent transcriptional activation. (C) Assessment of repression activity by various Hand2-MyoR chimeric Gal4 constructs. As expected, Gal4-MyoR represses and Gal4-Hand2 activates LexA-VP16 mediated transcriptional activity. A Gal4 fusion protein containing MyoR 1-100, which includes the N-terminal repression domain (75-100), and the C terminus of Hand2, potently repressed transcriptional activation mediated by LexA-VP16. In contrast, a Gal4 fusion protein containing the Hand2 N terminus fused with the MyoR C terminus, including the C-terminal repression domain, was unable to inhibit LexA-VP16 activation of reporter gene expression. (D) Protein alignment between amino acids 75 to 100 of MyoR and the corresponding region of Hand2 with conserved residues shaded black and similar residues shaded gray. Based on the alignment, MyoR contains a short peptide sequence (KKPLP) that is not present in Hand2.