FIG 8.
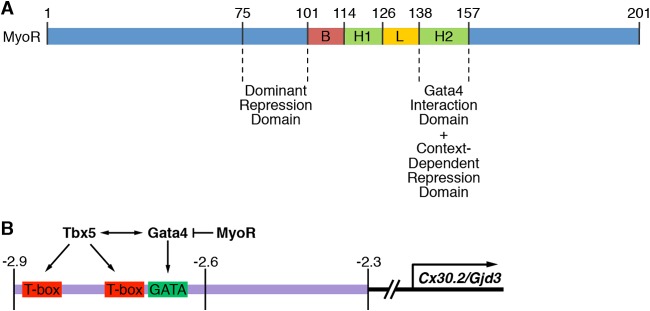
Model for MyoR-dependent regulation of Cx30.2 expression. (A) Summary of MyoR functional domains identified in the present study. Residues 138 to 157 serve as a Gata4 interaction and context-dependent repression domain. The domain encompassing amino acids 75 to 100 functions as a trans-repression domain even in a heterologous context. (B) Tbx5 and Gata4 regulate Cx30.2 expression via a 0.6-kb minimal regulatory element that directs expression to the AVN. Based on the present study, we propose that MyoR functions within AV nodal cells as a Gata4-specific transcriptional repressor to decrease Cx30.2 gene expression and thus modulate AV delay. Given the results of our protein-protein interaction experiments, we conclude that MyoR does not inhibit transcriptional activation by competing with Tbx5 for Gata4 interaction. Instead, we speculate that MyoR possesses a trans-repression domain that recruits as-yet unidentified corepressors to inhibit Gata4- and Tbx5-dependent activation of Cx30.2 expression.
