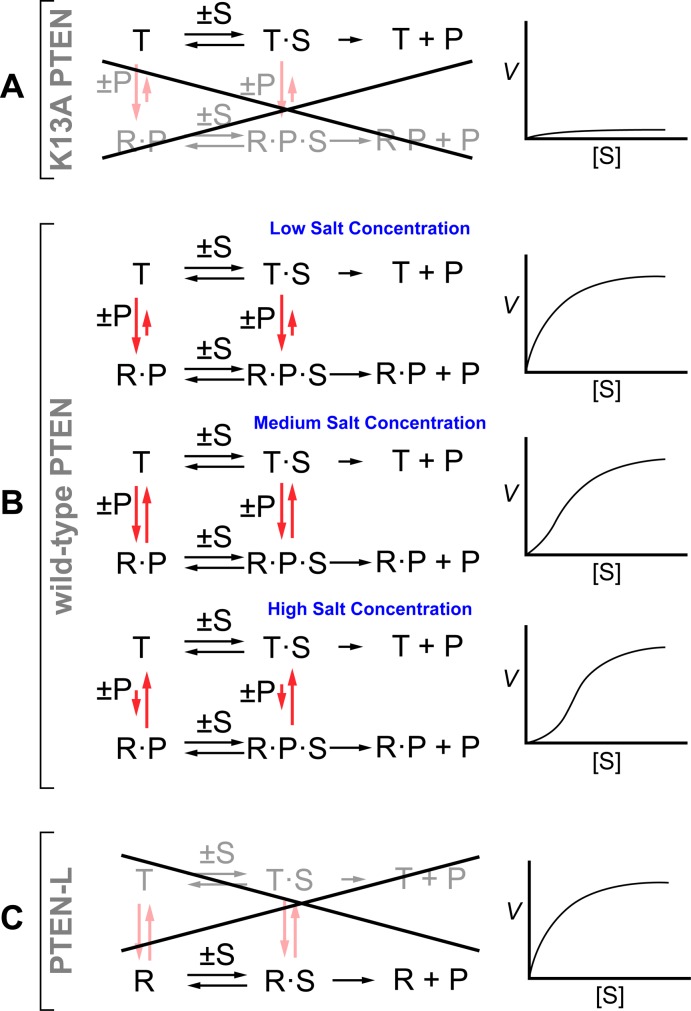
Figure 7. Notional schemes and diagrams for catalysis by K13A PTEN, wild-type PTEN, and PTEN-L.
(A) The binding motif for PIP2 (P) is absent in K13A PTEN. As a result, the K13A variant remains in its tense (T) state for all substrate concentrations at any salt concentration. (B) Wild-type PTEN has complex kinetic behavior. Low salt concentration favors the binding of PIP2. The wild-type enzyme is in its relaxed (R) state and exhibits Michaelis–Menten kinetics. Increasing salt concentration leads to decreasing affinity for PIP2 and a greater fraction of the enzyme being in the T state. As more PIP3 (S) is hydrolyzed, the increasing concentration of P leads to a greater fraction of the enzyme being in the R state. (C) PTEN-L is in the R state at any salt concentration and is unaffected by P.