Figure 2. Phosphorylation of tyrosine 295 and 361 of Dok1 correlates with suppression of CrkI transformation.
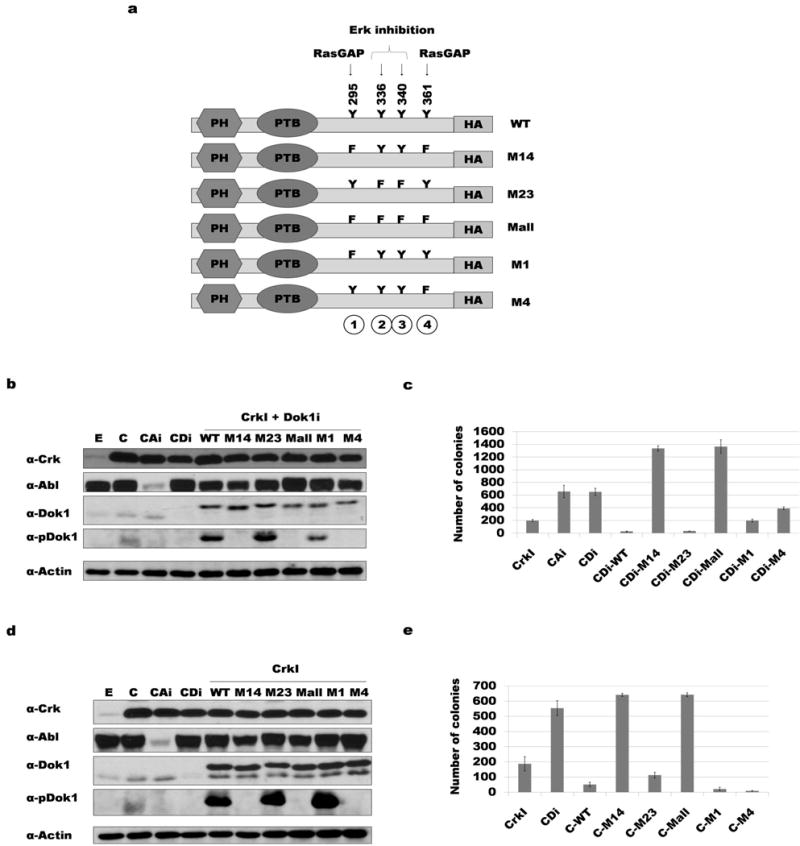
a) Diagram of the human Dok1 cDNA constructs used, indicating positions of tyrosine phosphorylation sites mutated. PH: Pleckstrin homology domain; PTB: phospho-tyrosine binding domain; Y: tyrosine; F: phenylalanine; HA: HA epitope tag. b) Dok1 knockdown and rescue with HA-tagged Dok1 constructs. NIH3T3 cell lysates were immunoblotted with antibodies indicated (αpDok1 = phosphospecific Dok1 antibody). E: empty vector control; C: CrkI transformed; CAi: CrkI-transformed, Abl knockdown; CDi: CrkI-transformed, Dok1 knockdown; WT: wild-type Dok1; M14: Y295F and Y361F mutant Dok1; M23: Y336F and Y340F mutant Dok1; M-all: Y295F, Y336F, Y340F and Y361F mutant Dok1; M1: Y295F mutant Dok1; M4: Y361F mutant Dok1. c) Soft agar colony formation results for cells in panel b. d) Over-expression of Dok1 in CrkI-transformed NIH3T3 cells; abbreviations as in panel b. e) Soft agar colony formation results for cells in panel d.
