Figure 5.
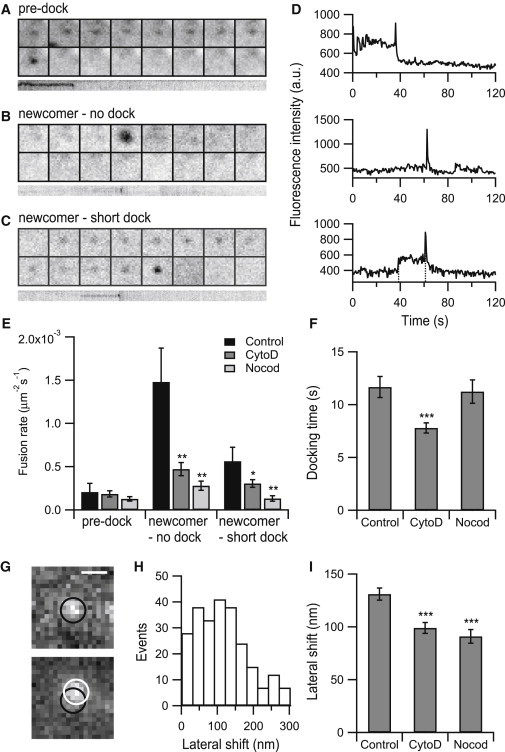
Disruption of the actin or microtubule network reduces the fusion of newcomer vesicles. (A–C) Example images of predock fusion, newcomer-no dock fusion, and newcomer-short dock fusion. (D) Central intensity profiles of (A–C). For newcomer-short dock fusion, the interval between the two dashed lines in (D) was calculated as the docking time. (E) Average fusion rate of each type of fusion for each condition. (n = 1016 events from 6 cells for control, n = 476 events from 9 cells for CytoD treatment, and n = 285 events from 8 cells for Nocod treatment). (F) Average docking time for each condition (n = 131 events from 3 cells for control, n = 150 events from 9 cells for CytoD treatment, and n = 79 events from 8 cells for Nocod treatment). (G) Example of lateral shift of a fusing vesicle. The displacement from the last position before fusion (black circle) to the final fusion site (white circle) was 114 nm. Scale bar, 500 nm. (H) Distribution of the lateral shift in control cells. (I) Average lateral shift for each condition. (n = 262 events from 3 cells for control, n = 223 events from 9 cells for CytoD treatment, and n = 129 events from 8 cells for Nocod treatment). Error bars are ±SE. p values were determined using Student’s t-test. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, and ∗∗∗p < 0.001.
