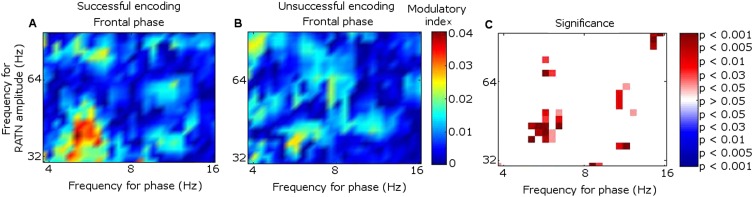
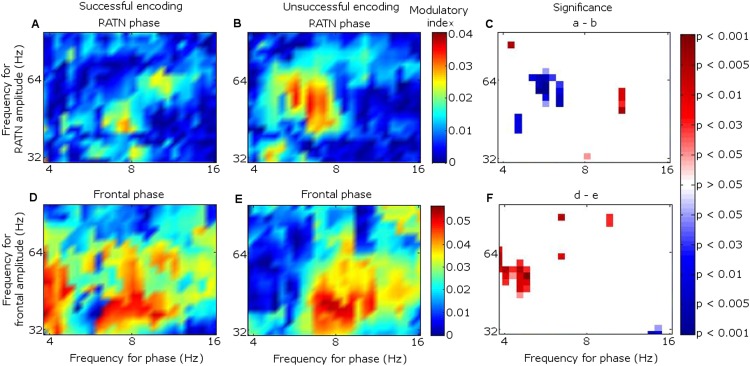
Figure 3. Frontal-right anterior thalamic nucleus (RATN) cross-frequency coupling (CFC).
(A) Successful encoding. (B) Unsuccessful encoding. (C) Paired T-tests: Successful minus unsuccessful encoding.
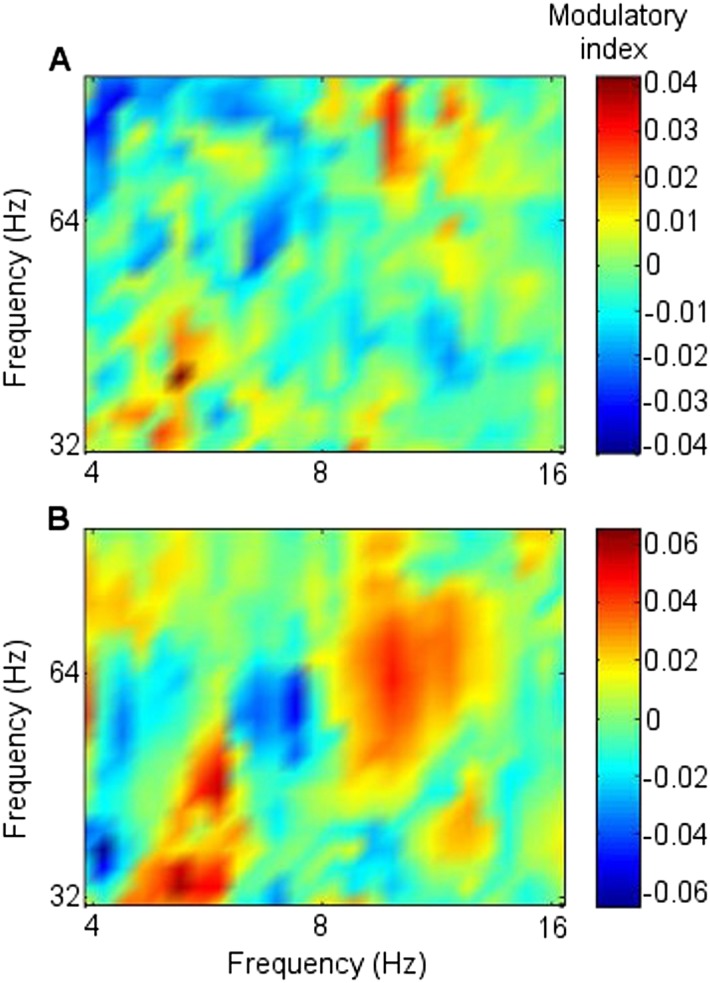
Figure 3—figure supplement 1. Cross-frequency coupling (CFC) within right anterior thalamic nucleus (RATN) and within frontal neocortex.
Figure 3—figure supplement 2. Cross frequency coupling (CFC) during successful encoding in Participant 7.
Figure 3—figure supplement 3. Cross-frequency coupling (CFC) with differing frontal cortical sites.