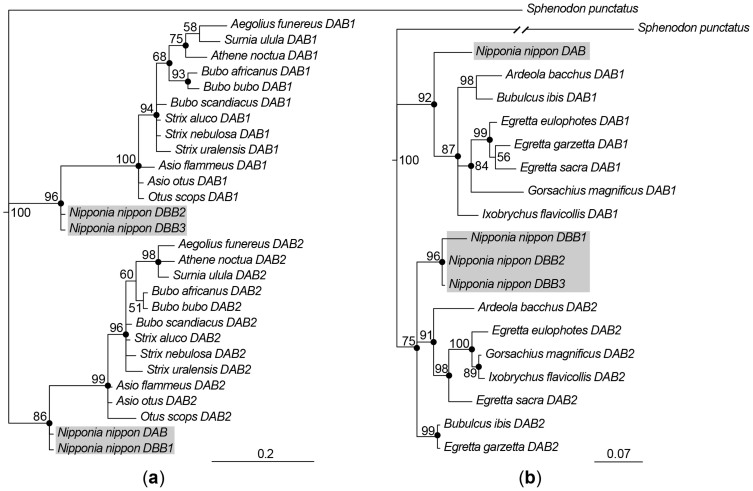
Figure 5. Phylogenetic trees for IIβ exon 3 (a) and exon 2 (b) nucleotide sequences.
Numbers beside nodes indicate Bayesian support (%), and the filled circles on the nodes represent bootstrap values higher than 50% in maximum likelihood analysis. The crested ibis sequences are shaded. (a) The exon 3 tree includes crested ibis and owl sequences. Accession numbers of analyzed species are as follows: Aegolius funereus, EF641252, EF641253; Asio flammeus, EF641250, EF641251; Asio otus, EF641223, EF641224; Athene noctua, EF641247, EF641248; Bubo africanus, EF641244, EF641245; Bubo bubo, EF641236, EF641238; Bubo scandiacus, EF641233, EF641235; Otus scops, EF641257, EF641259; Strix aluco, EF641254, EF641256; Strix nebulosa, EF641240, EF641241; Strix uralensis, EF641242, EF641243; Surnia ulula, EF641226, EF641230; Sphenodon punctatus, DQ124232. (b) The exon 2 tree included the crested ibis and Ardeid sequences excluding the antigen-binding sites. Sequence sources are: Ardeola bacchus, HM991020, HM991044; Bubulcus ibis, HM991033, HM991054; Egretta eulophotes, HM991028, HM991052; Egretta garzetta, HM991035, HM991056; Egretta sacra, HM991037, HM991058; Gorsachius magnificus, HM991024, HM991048; Ixobrychus flavicollis, HM991026, HM991050; Sphenodon punctatus, DQ124231.