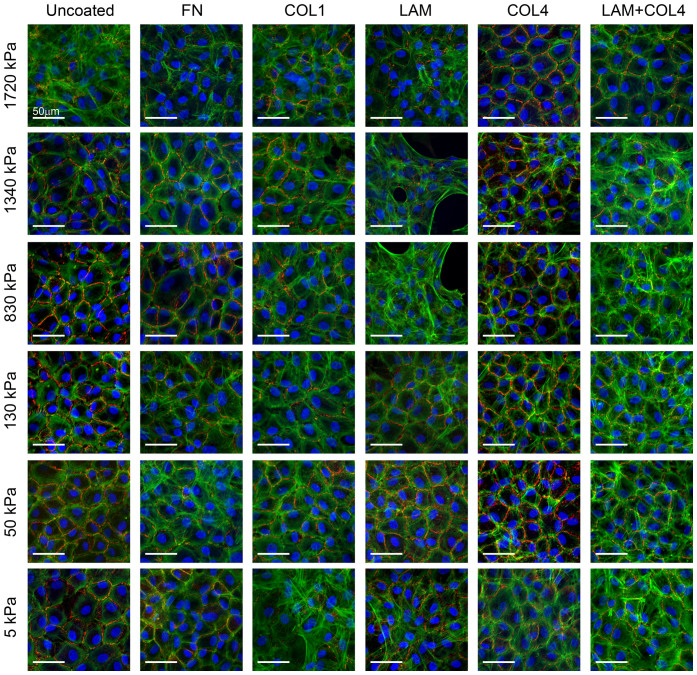
Figure 2. Screening the response of CE cells to variable substrate elastic modulus and ECM protein coating.
CE cells were cultured on one of 36 different PDMS substrates with elastic modulus of 5, 50, 130, 830, 1340 or 1720 kPa and uncoated or coated with the ECM proteins fibronectin (FN), collagen type I (COLI), laminin (LAM), collagen type IV (COL4) or LAM and COL4. Representative fluorescent images show CE cells stained for nuclei (blue), ZO-1 (red) and F-actin (green), demonstrating distinct differences in morphology based on the substrates properties. In general, CE cells appeared to have a more polygonal morphology, continuous ZO-1 at the cell-cell border and cortical F-actin on substrates with an elastic modulus of 50 kPa for most of the ECM proteins. Similar results were observed for the COL4 coating for most of the elastic modulus formulations. Thus, the combination of elastic modulus and ECM protein that gave the best results in terms of the CE cell morphology most closely resembling that observed in vivo was an elastic modulus of 50 kPa and COL4 coating, which was selected for further cell expansion studies.