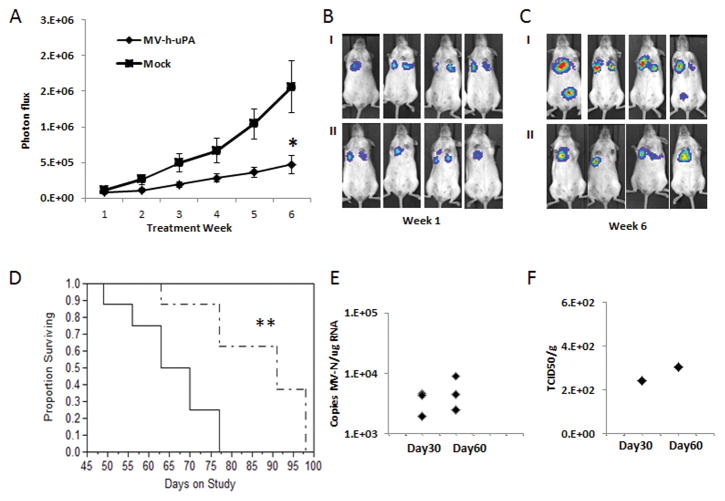
Figure 5. In vivo anti-metastasic effects in Xenograft metastases models.
(A). The MDA-MB-231 experimental lung metastases model was established as described in methods. Mice were (n= 8/group) treated with three IV injections (every other day) of vehicle or MV-h-uPA. Lung metastases progression was assessed by in vivo bioluminescence imagingat weeks 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6 after treatment. *p=0.0093 (week 6). (B, C) Representative pictures of differences in lung metastases progression at week 1 (B) and 6 (C) by in vivo Bioluminescence imaging. I: Control. II: MV-h-uPA. (D). Kaplan-Mier analysis of survival of tumor bearing mice treated with vehicle control or MV-h-uPA. MV-h-uPA vs. control ** p=0.0057. (E) Total RNA was extracted from lung tissues for qRT-PCR analysis of MV-N mRNA. Results were expressed as copies of MV-RNA/μg of total RNA in each organ/tissue. (F) Infectious virus recovery from lung tissues after MV-m-uPA administration. Viral titers are displayed as TCID50/ gram of tissue.