Figure 4. LC-MRM and Nephelometry Have Similar Sensitivity for Detection of Treatment Response in an IgE MM Patient.
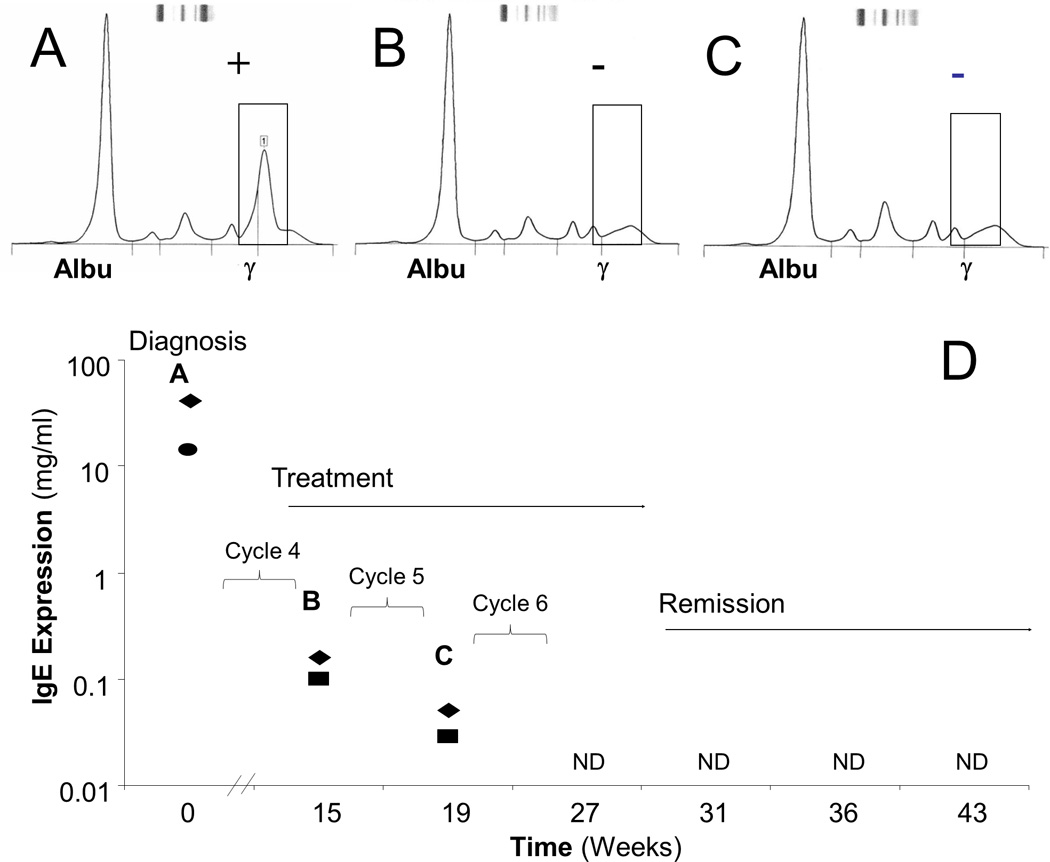
The patient was monitored over time with SPEP (A–C) as well as nephelometry and LC-MRM (D) starting at the time of diagnosis and continuing through the treatment regimen of a clinical trial combining a proteasome inhibitor and an immunomodulator. Both SPEP (circle) and LC-MRM (diamonds) results show IgE elevation at diagnosis (A). During treatment (B and C), the SPEP is negative, but elevated IgE is still detected by nephelometry (squares) and LC-MRM (D, letters A–C indicate quantification from the same serum samples as the SPEP data panels above) are still able to detect elevated IgE. Nephelometry and LC-MRM can observe the decrease in tumor burden after the 5th cycle of treatment, and IgE is not detected (ND) in the patient serum by either method after the 6th cycle of therapy. Tumor burden is reduced by three orders of magnitude, before the immunoglobulin is no longer detected.
