Figure 1.
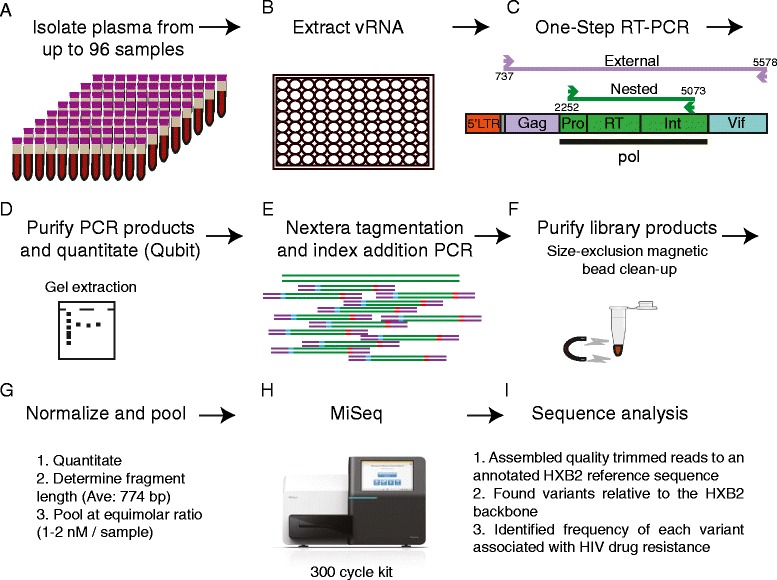
Preparation and sequencing of samples. (A) Plasma is isolated from whole blood from up to 96 samples. (B) Viral RNA is isolated from up to 1 ml of plasma. (C) Viral RNA is used in a one-step RT-PCR amplification of a 2.8 kb region of the pol gene. When nested PCR is required, a 4.8 kb region is amplified as an external PCR followed by the 2.8 kb nested PCR of the pol gene. (D) PCR products are purified either by gel electrophoresis followed by gel extraction or through size-exclusion magnetic beads and then quantitated using the Qubit system. (E) Purified products are randomly fragmented and subjected to a limited cycle PCR to add sequencing adaptors and indices used for multiplexing samples. (F) Newly created libraries are purified by size-exclusion magnetic beads to remove short fragments. (G) The average size of the library fragments are calculated by bioanalysis and final concentration of the libraries calculated by Qubit are used to normalize each library and pool multiple libraries together at equimolar ratios. (H) Libraries are sequenced on the Illumina MiSeq. (I) Geneious Pro Software is used to trim sequencing reads based on quality scores and assemble the reads to a HXB2 reference sequence annotated with HIV drug resistance mutations. Geneious is used to identify variants within each sample relative to HXB2. Finally, variants associated with drug resistance mutations were extracted and their frequencies noted. Details about the analysis parameters are outlined in the Methods section.
