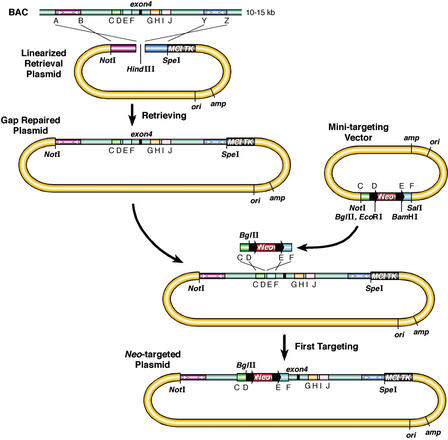
Figure 2.
An improved procedure for subcloning DNA from BACs and for constructing cko-targeting vectors. The homology arms used for gap repair (subcloning) and for targeting, are PCR-amplified from BAC DNA. The two homology arms (purple or dark blue), amplified using primers A and B or primers Y and Z, were cloned into an MC1TK-containing plasmid, to generate the gap repair (retrieval) plasmid for subcloning. The gap repair plasmid was linearized with HindIII to create a DNA double-strand break for gap repair. A minitargeting vector was constructed by ligating together the two PCR products generated by amplification of BAC DNA with primers C and D (light green) or primers E and F (blue), a floxed Neo selection cassette (black arrow: loxP site), and pBluescript. A BglII restriction site was included in the minitargeting vector for diagnosing gene targeting in ES cells. The black arrows denote loxP sites. The targeting cassette was excised by NotI and SalI digestion, or by PCR amplification, using primers C and F. The gap-repaired plasmid and the excised targeting cassette were cotransformed into recombination-competent DY380 or EL350 cells. The recombinants had a floxed Neo cassette inserted between primers D and E and can be selected on kanamycin plates. The Neo cassette was excised with Cre recombinase, leaving a single loxP site at the targeted locus (see Fig. 3). Similarly, a Neo selection cassette can be inserted between primers H and I using homology arms amplified by primers G, H (light orange), and I, J (light purple).