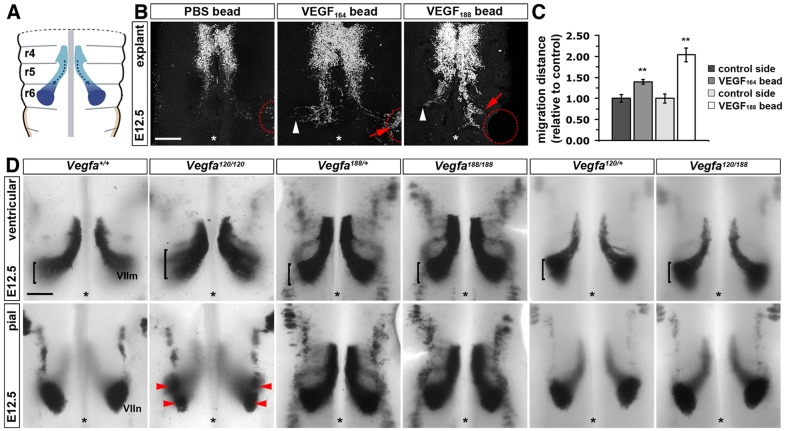
Fig. 2.
VEGF188 is sufficient for FBM neuron migration. (A) Schematic representation of FBM neuron migration in the mouse. (B) ISL1 staining of E12.5 hindbrain explants containing implanted heparin beads soaked in PBS (n=10) or PBS containing VEGF164 (n=10) or VEGF188 (n=6). Red dotted circles indicate the position of heparin beads; white arrowheads indicate normal migration; red arrows indicate migration towards heparin beads; asterisks indicate the midline. Scale bar: 200 µm. (C) Distance migrated by FBM neurons. Migration distance was quantified as migration away from r5 territory on the hindbrain side with a bead relative to the control half of the same hindbrain; mean±s.e.m. control 1±0.09 versus VEGF164 bead 1.39±0.05; control 1±0.11 versus VEGF188 bead 2.04±0.17; **P<0.01, VEGF compared with control (t-test). (D) Whole-mount Isl1 in situ hybridisation of E12.5 hindbrains of the indicated genotypes detects migrating FBM neurons (VIIm) (control, n=10; Vegfa120/120, n=6; Vegfa188/188, n=4; Vegfa120/188, n=5). Brackets indicate the width of the neuronal stream on the ventricular side; red arrowheads indicate dumbbell-shaped nuclei on the pial side; asterisks indicate the midline. Scale bar: 25 µm.