Fig. 3.
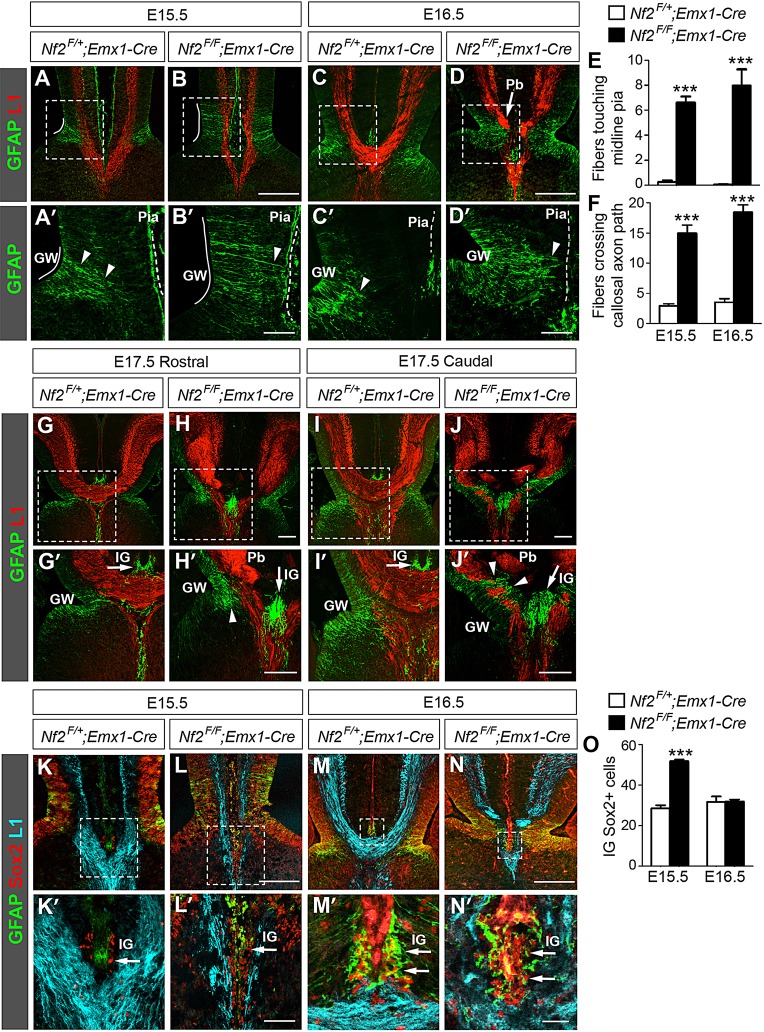
Nf2 loss impairs glial wedge development. (A,A′) In control embryos at E15.5, GFAP+ processes (arrowhead) from the glial wedge (GW, white line) have detached from the pia (dashed line). At this stage, the GFAP antibody often stains the pia nonspecifically. Panels labeled with primes are the magnified view of the boxed areas in corresponding panels. (B,B′) In Nf2F/F;Emx1-Cre embryos, the GW is elongated and many GW processes remain attached to the pia and intersect L1+ callosal axons (B′, arrowhead). (C-D′) In E16.5 Nf2F/F;Emx1-Cre embryos, GW fibers still extend close to the pia (D′, arrowhead) and Probst bundles (Pb) are formed (D, arrow). (E,F) More GFAP+ GW fibers touch the midline pia (E, n=4) and more cross callosal axon path (F, n=6) in Nf2F/F;Emx1-Cre embryos than in controls. ***P<0.001. (G-J′) In E17.5 Nf2F/F;Emx1-Cre brains, GW fibers have lost pial attachment in rostral regions (H′, arrowhead) but still project close to the pia and intersect axons of the corpus callosum or hippocampal commissure in caudal regions (J′, arrowhead). Arrow: indusium griseum (IG). (K-L′) At E15.5, Sox2+ cells are present in the IG primordium in control and Nf2F/F;Emx1-Cre embryos (arrow). These cells are GFAP− at this stage. (M-N′) GFAP+ IG astrocytes (arrow) are present in control and Nf2F/F;Emx1-Cre embryos at E16.5. Most of these cells also express Sox2. (O) The number of IG Sox2+ cells is increased in Nf2F/F;Emx1-Cre embryos at E15.5 (n=5) but is similar to that in controls at E16.5 (n=4). Scale bars: 200 µm in B,D,H,H′,J,J′,L,N; 50 µm in B′,D′,L′; 10 µm in N′.