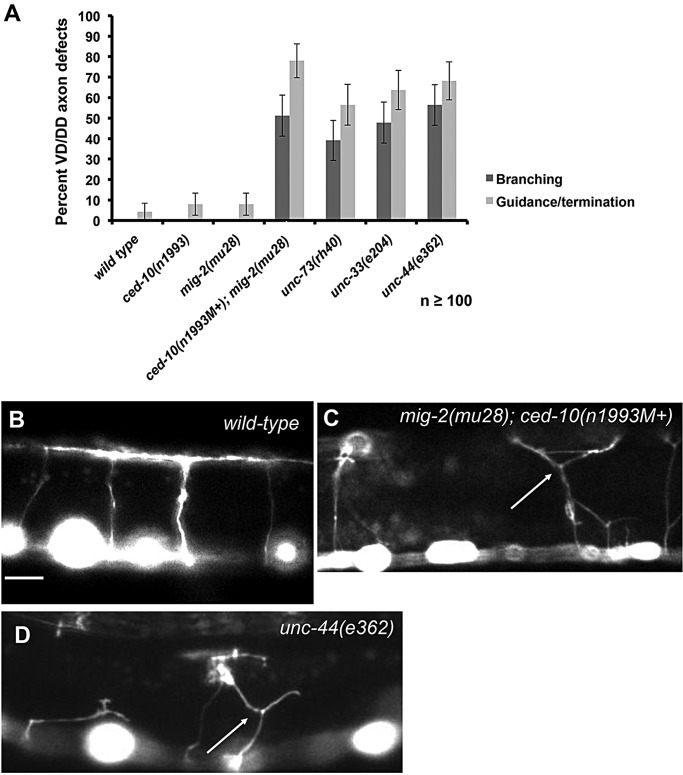
Fig. 3.
Mutations with increased growth cone protrusion cause ectopic axon branching. (A) Quantification of VD/DD axon pathfinding defects (guidance and premature termination) and ectopic axon branching in young adults. At least 100 axons were scored. Error bars represent 2× standard error of proportion. (B-D) Representative fluorescence micrographs of VD/DD axons demonstrating axon pathfinding and branching errors. (B) Wild-type, (C) mig-2(mu28); ced-10(n1993M+) and (D) unc-44(e362) VD/DD axons. Arrows point to ectopic axon branches. Dorsal is up, and anterior is left. M+ indicates that the animals had wild-type maternal ced-10(+) activity. Scale bar: 10 µm.