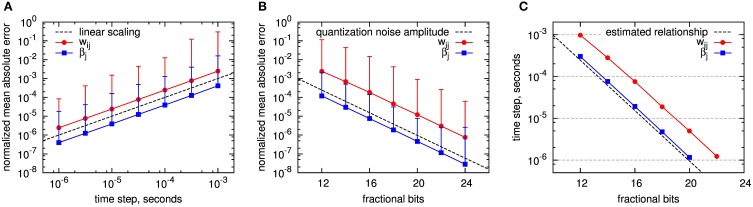
Figure 6.
Accuracy of fixed step size simulation with Euler method and event-driven analytic simulation using fixed point operands. The accuracy of wij and βj is assessed by the normalized mean absolute error taken over a large set of experiments with the exact analytical solution as reference, see text for details. (A) Simulation with Euler, dependent on step size. The dashed line shows the linear scaling: y(dt) = dt · s−1. (B) Analytical solution with event-driven update (analytical II) using fixed-point representation with different counts of fractional bits. The dashed line shows the quantization noise amplitude: y(b) = 2−b. The error bars in A and B denote the normalized maximum absolute error recorded within all simulations per setup. (C) Comparison between the errors introduced by the Euler method and the use of fixed-point numbers with limited number of fractional bits: For wij and βj the location of equal mean absolute errors is plotted, depending on the step size for the Euler method, respectively the number of fractional bits of the fixed-point implementation. Dashed line: estimated relationship according to Equation (60).