Figure 3.
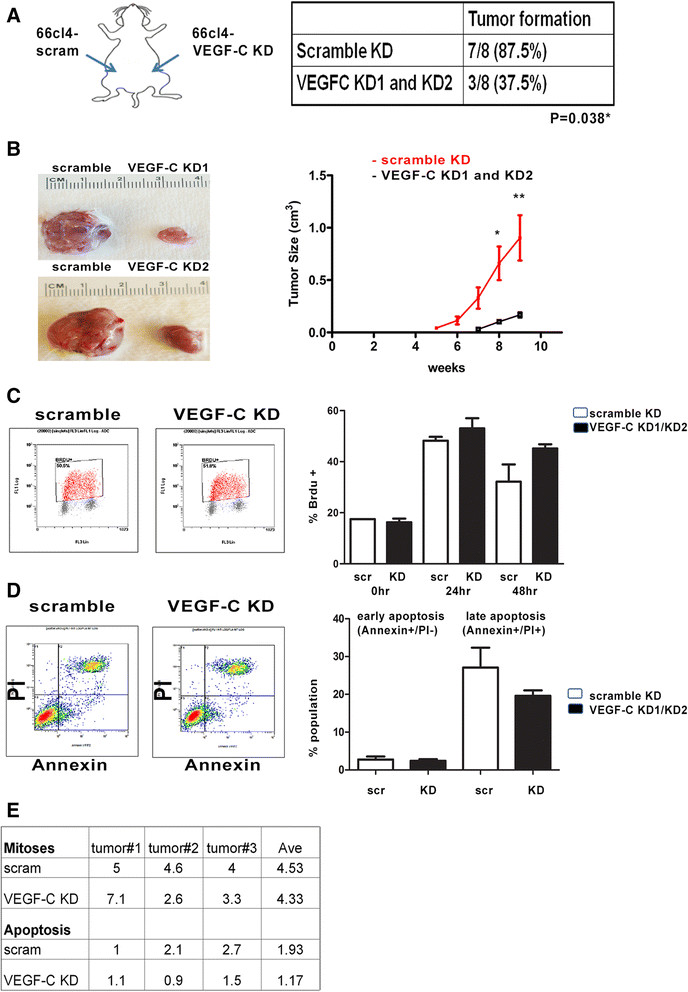
Vascular endothelial growth factor C-knockdown in 66 cl4 mouse mammary carcinoma cells decreases tumor growth and tumor formation in vivo . (A) Tumor formation efficiency of ten cells from 66 cl4-scram and 66 cl4-VEGF-C KD1/2 cells injected into the left and right mammary fat pads of female BALB/c mice. The experiment was ended at week 9 after injection because of the large primary tumor sizes in the control group. scr, Scramble; VEGF-C KD, Vascular endothelial growth factor C knockdown. (B) Representative picture of 66 cl4-scram and 66 cl4-VEGF-C KD1 and KD2 tumors derived from the left and right mammary fat pads of the same animal (left). Tumor growth in the mice was measured using calipers and calculated using the formula V = 1/2(W)(W)(L) (right). *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01. (C) Representative flow data show results of a bromodeoxyuridine (BrdU) assay performed on 66 cl4-scram cells, as well as on VEGF-C KD1 and KD2 cells, combined as KD1/2 (left). BrdU-positive populations from 66 cl4-scram and VEGF-C KD1/2 cells at 0, 24 and 48 hours after release from serum starvation are shown. Data were quantified from two independent experiments with duplicates in the control and two different short-hairpin RNA cell lines. (D) Representative flow data from a fluorescein isothiocyanate-annexin V apoptosis assay (left). Quantification of the apoptosis assay is shown from two independent experiments with duplicates for detection of the early and late apoptotic populations in the 66 cl4-scram and VEGF-C KD1 and KD2 cells (data combined as KD1/KD2). PI, Propidium Iodide. (E) Quantification of mitotic and apoptotic cells is shown from 66 cl4-scram and 66 cl4-VEGF-C KD tumors. Mitotic and apoptotic cells were counted in ten high-power fields per hematoxylin and eosin-stained section. Three control and three VEGF-C KD tumors were counted and analyzed in total. Ave, Average.
