Figure 4.
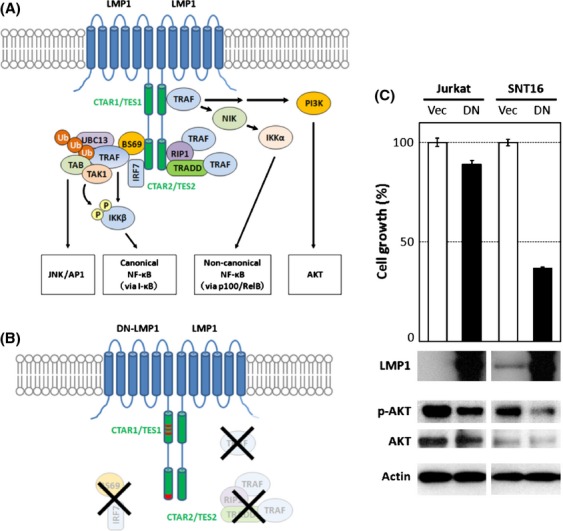
Dominant negative LMP1 inhibits proliferation of CAEBV T cells. (A) An illustration of the LMP1 signal pathway. LMP1 molecules form an oligomer that is required for its signaling activity (the oligomer is designated as a dimer for simplification). (B) DN-LMP1 has point mutations that modify the PXQXT motif in the TES1 domain to AXAXT and the YYD in the tail of TES2 to IID, resulting in the dysregulated signaling activity. (C) The growth rates of Jurkat and SNT16 cells were assessed after transient transfection with empty vector (Vec) or DN-LMP1 (DN). Experiments were performed in triplicate and data are presented as means with standard errors. Western blotting results for the expression of LMP1, phospho-AKT (pAKT), AKT, and actin are shown underneath the growth bars.
