Figure 1.
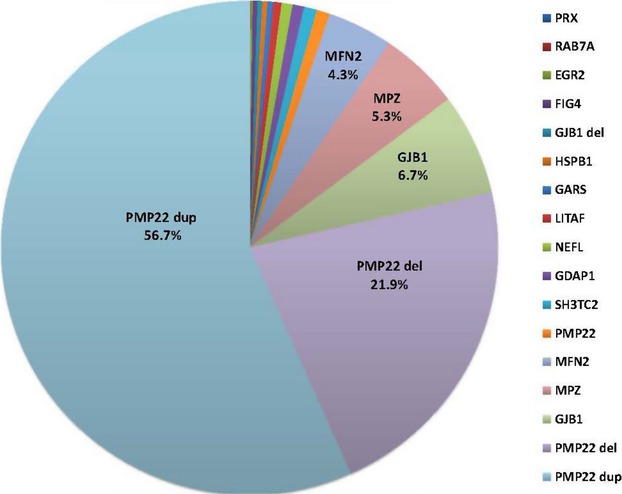
The mutation frequency of Charcot–Marie–Tooth disease genes in a large cohort (n = 17,377) analyzed at a commercial laboratory. The pie chart shows the percentage of positive results attributed to each gene by color out of the total number of genetically positive patients (n = 3216) as determined by Sanger sequencing and MLPA. Mutations in four genes (PMP22 dup/del, GJB1, MPZ, and MFN2) accounted for 94.9% of the genetically positive patients in our cohort. PMP22 duplications (dup) accounted 56.7% of positive patients, PMP22 deletions (del) 21.9%, GJB1 6.7%, MPZ 5.3%, MFN2 4.3%, PMP22 0.9%, SH3TC2 0.8%, GDAP1 0.7%, NEFL 0.7%, LITAF 0.5%, GARS 0.4%, HSPB1 0.3%, GJB1 del 0.3%, FIG4 0.3%, EGR2 0.1%, RAB7A 0.1%, and PRX 0.03%.
